Synthesis of Diversely Substituted Diethyl (Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Phosphonates
- PMID: 40363884
- PMCID: PMC12073250
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30092078
Synthesis of Diversely Substituted Diethyl (Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Phosphonates
Abstract
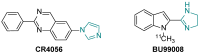
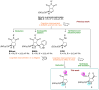
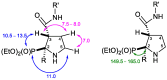
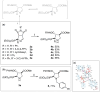
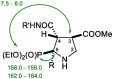
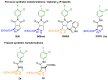
Imidazoline I2 receptors (I2-IR) are untapped therapeutic targets lacking a structural description. Although the levels of I2-IR are dysregulated in a plethora of illnesses, the arsenal of ligands that can modulate I2-IR is limited. In this framework, we have reported several new structural families embodying the iminophosphonate functional group that have an excellent affinity and selectivity for I2-IR, and selected members have demonstrated relevant pharmacological properties in murine models of neurodegeneration and Alzheimer's disease. Starting with these iminophosphonates, we continued to exploit their high degree of functionalization through a short and efficient synthesis to access unprecedented 2,3-di, 2,2,3-tri, 2,3,4-tri, and 2,2,3,4-tetrasubstituted diethyl (pyrrolidine-2-yl) phosphonates. The stereochemistry of the new compounds was unequivocally characterized by X-ray crystallographic analyses. Two selected compounds with structural features shared with the starting products were pharmacologically evaluated, allowing us to deduce the required key structural motifs for biologically active aminophosphonate derivatives.
Keywords: (pyrrolidine-2-yl)phosphonate; imidazoline I2 receptor ligand; phosphonic ester; phosphoproline; pyrroline; α-aminophosphonate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abás S., Rodríguez-Arévalo S., Bagán A., Griñán-Ferré C., Vasilopoulou F., Brocos-Mosquera I., Muguruza C., Pérez B., Molins E., Luque F.J., et al. Bicyclic α-Iminophosphonates as High Affinity Imidazoline I2 Receptor Ligands for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2020;63:3610–3633. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02080. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rovati L.C., Brambilla N., Blicharski T., Connell J., Vitalini C., Bonazzi A., Giacovelli G., Girolami F., D’Amato M. Efficacy and Safety of the First-in-Class Imidazoline-2 Receptor Ligand CR4056 in Pain from Knee Osteoarthritis and Disease Phenotypes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020;28:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Spain, PID2022-1380790B-I00 MICIU/AEI /10.13039/501100011033 and FEDER, UE and PDC2022-133441-I00 MICIU/AEI /10.13039/501100011033 Europea Next Genera-tionEU/ PRTR/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades, Agencia Estatal de Investigación
- IT1512/22/the Basque Government
- 2021 SGR 00357/Generalitat de Catalunya
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

