The Multidisciplinary Approach to Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis
- PMID: 40363936
- PMCID: PMC12072366
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14092904
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis
Abstract
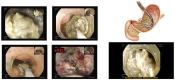
Acute pancreatitis is a common gastrointestinal condition, primarily caused by gallstones and alcohol abuse, with other causes including hypertriglyceridemia, trauma, infections, etc. While most cases are mild and self-limiting, up to 20% of patients develop severe pancreatitis with pancreatic necrosis, increasing the risk of multi-organ failure and mortality. Conservative management involves fluid resuscitation, nutritional support, and antibiotics for infected peripancreatic fluid collections (PFCs). When PFCs are infected or symptoms persist, invasive interventions such as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage or percutaneous drainage are recommended. Dual modalities (endoscopic and percutaneous drainage) offer better outcomes with fewer complications. Direct endoscopic necrosectomy is considered for patients who do not improve with drainage. A multidisciplinary team, including endoscopists, interventional radiologists, surgeons, and specialists, is essential for optimal management of severe necrotizing pancreatitis.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; direct endoscopic necrosectomy; endoscopic drainage; necrotizing pancreatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Management of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis in the Intensive Care Unit: A Narrative Review—PubMed. [(accessed on 19 December 2024)]; Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.beilinson.idm.oclc.org/31238118/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

