PCSK9 Inhibitors "Fast Track" Use Versus "Stepwise" Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Retrospective Single-Center Study in a "Real-World" Population
- PMID: 40364024
- PMCID: PMC12072999
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14092992
PCSK9 Inhibitors "Fast Track" Use Versus "Stepwise" Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Retrospective Single-Center Study in a "Real-World" Population
Abstract
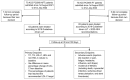
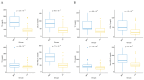
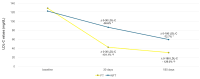
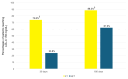
Background: The "fast track" addition (within 48 h) of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors (PCSK9i) to the optimized oral lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) during hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome (ACS) has been shown to rapidly achieve the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) therapeutic targets. However, so far, its efficacy in real-world settings remains understudied. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 128 ACS patients treated at our center, comparing "PCSK9i fast track" use within 48 h to standard "stepwise" LLT. Lipid levels and incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) were evaluated at 30 and 180 days. Results: The "PCSK9i fast track" group achieved significantly lower LDL-C levels at 30 days (41.5 ± 27.5 vs. 85.6 ± 35.9 mg/dL, p < 0.001) and 180 days (29.6 ± 21.0 vs. 59.0 ± 32.4 mg/dL, p < 0.001). Recommended LDL-C targets (<55 mg/dL) were met by 88.3% of the "PCSK9i fast track" group at 180 days, compared with 61.9% of controls (p < 0.001). No significant differences in MACEs were observed between groups. No adverse effects from PCSK9i use were noted. Conclusions: The "PCSK9i fast track" strategy was safe and effective in achieving LDL-C targets more rapidly than conventional approaches in real-world ACS patients.
Keywords: LDL-C; PCSK9i; acute cardiovascular syndrome; dyslipidemia; “fast track” strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strike early-strike strong lipid-lowering strategy with proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors in acute coronary syndrome patients: real-world evidence from the AT-TARGET-IT registry.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024 Nov 11;31(15):1806-1816. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae170. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38788773
-
Real-world treatment patterns of PCSK9 inhibitors among patients with dyslipidemia in Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom.Curr Med Res Opin. 2019 May;35(5):829-835. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1532885. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019. PMID: 30289004
-
Lipoprotein Apheresis and Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors in Patients With Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A One Center Study.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;26(1):51-58. doi: 10.1177/1074248420943079. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32729335
-
PCSK9 Inhibitors: Is the Time Ripe for the "Fast Track" Use Independently on the LDL-C Baseline Values in Acute Coronary Syndrome?High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024 Nov;31(6):695-699. doi: 10.1007/s40292-024-00676-8. Epub 2024 Oct 4. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024. PMID: 39365527 Review.
-
Impact of early initiation of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review meta-analysis.Indian Heart J. 2023 Nov-Dec;75(6):416-422. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2023.09.005. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Indian Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37777180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Bijl P., Abou R., Goedemans L., Gersh B.J., Holmes D.R., Jr., Marsan N.A., Delgado V., Bax J.J. Left Ventricular Post-Infarct Remodeling: Implications for Systolic Function Improvement and Outcomes in the Modern Era. JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8:131–140. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.08.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sabatine M.S., De Ferrari G.M., Giugliano R.P., Huber K., Lewis B.S., Ferreira J., Kuder J.F., Murphy S.A., Wiviott S.D., Kurtz C.E., et al. Clinical Benefit of Evolocumab by Severity and Extent of Coronary Artery Disease: Analysis From FOURIER. Circulation. 2018;138:756–766. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034309. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laufs U., Catapano A.L., De Caterina R., Schiele F., Sionis A., Zaman A., Jukema J.W. The effect of the 2019 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal achievement in patients with acute coronary syndromes: The ACS EuroPath IV project. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2023;148:107141. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107141. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferlini M., Munafò A., Varbella F., Delnevo F., Solli M., Trabattoni D., Piccaluga E., Cardile A., Canova P., Rossini R., et al. Achievement of target LDL-cholesterol level in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: The JET-LDL registry. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024;397:131659. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131659. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

