A Comprehensive Review of the Effects of Hyoscine Butylbromide in Childhood
- PMID: 40364041
- PMCID: PMC12072732
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14093009
A Comprehensive Review of the Effects of Hyoscine Butylbromide in Childhood
Abstract
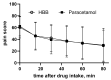
Background/Objectives: Hyoscine butylbromide (HBB) is a spasmolytic drug classified as indispensable by the World Health Organization. While mostly used in adults, it is also approved for use in adolescents and children aged 6 years and older. We have comprehensively reviewed the efficacy and safety of HBB in approved and off-label childhood indications. Results: Childhood studies covered an age range starting as early as 2 days. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) found a similar efficacy compared to paracetamol in the approved indication of abdominal cramps and pain. Among off-label uses, several studies demonstrate efficacy in general anesthesia and various diagnostic procedures, but the largest body of evidence relates to use in childbirth/labor, including 17 RCTs. While these largely focused on efficacy outcomes on the mother, fetal safety outcomes were reported in 12 of these studies, mostly as effects on the APGAR score and/or heart rate. The overall evidence supports safety in infants and children including those younger than the approved use age of 6 years and older. Conclusions: While only limited pediatric efficacy data from RCTs are available in the approved indications, data from thousands of patients in RCTs, case series, and non-randomized trials do not raise concerns on the safety and tolerability of HBB in childhood. Additional dedicated childhood studies, particularly RCTs, on efficacy are recommended.
Keywords: abdominal cramps; abdominal pain; childbirth; children; hyoscine butylbromide; infants; vomiting.
Conflict of interest statement
R.V.F. has received support to attend courses, grants for research, act as a speaker or as part of advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Bayer, BioGaia, Biopas, Carnot, Chinoin, Columbia, Ferrer, Ipsen, Mayoly-Spindler, Medix, Megalabs, Nestlé, Nestlé Nutrititon Institute, Nutricia/Stendhal, Opella (a Sanofi company), Reckitt Benckiser/Mead Johnson, Sanofi, Schwabe Pharma, and Takeda. A.H. has received support to attend courses, grants for research, act as a speaker or part of advisory board for Abbvie, Danone, Ipsen, Janssen, Mirum, Orphalan, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda. C.B.M. has received support to attend courses, grants for research, act as a speaker or as part of advisory boards from Abbott, Bayer, Biocodex, Biogaia, B-Life, Carnot, Cassará, Danone, Nestlé, Nutricia, Opella (a Sanofi company), Reckitt Benckiser/Mead Johnson Sanofi, and Siegfried. M.C.M. is a paid consultant to Opella, a Sanofi company, on several projects including the project reflected in this manuscript. MCM has not, however, received a honorarium for authorship of this paper. Opella (a Sanofi company) had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Weiser T. Guideline recommendations for the treatment of abdominal pain (in irritable bowel syndrome) Evid. Self-Med. 2021;1:210010. doi: 10.52778/efsm.21.0264. - DOI
-
- Barbara G., Cremon C., Bellini M., Corsetti M., Di Nardo G., Falangone F., Fuccio L., Galeazzi F., Iovino P., Sarnelli G., et al. Italian guidelines for the management of irritable bowel syndrome: Joint Consensus from the Italian Societies of: Gastroenterology and Endoscopy (SIGE), Neurogastroenterology and Motility (SINGEM), Hospital Gastroenterologists and Endoscopists (AIGO), Digestive Endoscopy (SIED), General Medicine (SIMG), Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Pediatric Nutrition (SIGENP) and Pediatrics (SIP) Dig. Liver Dis. 2023;55:187–207. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2022.11.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schäfer E., Ewe K. The treatment of irritable colon. Efficacy and tolerance of buscopan plus, buscopan, paracetamol and placebo in ambulatory patients with irritable colon. Fortschr. Med. 1990;108:488–492. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

