Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign
- PMID: 40364054
- PMCID: PMC12072632
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14093021
Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign
Abstract
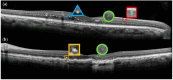
Background: Hyperreflective retinal foci (HRF) are small, discrete, hyperreflective elements observed in the retina using optical coherence tomography (OCT). They appear in many retinal diseases and have been linked to disease progression, treatment response, and prognosis. However, their definition and clinical use vary widely, not just between different diseases, but also within a single disorder. Methods: This perspective is based on a review of peer-reviewed studies examining HRF across different retinal diseases. The studies included analyzed HRF morphology, distribution, and clinical relevance using OCT. Particular attention was given to histopathological correlations, disease-specific patterns, and advancements in automated quantification methods. Results: HRF distribution and features vary with disease type and even within the same disease. A variety of descriptions have been proposed with different characteristics in terms of dimensions, reflectivity, location, and association with back shadowing. Automated OCT analysis has enhanced HRF detection, enabling quantitative analysis that may expand their use in clinical practice. However, differences in software and methods can lead to inconsistent results between studies. HRF have been linked to microglial cells and may be defined as neuro-inflammatory cells (Inflammatory, I-HRF), migrating retinal pigment epithelium cells (Pigmentary, P-HRF), blood vessels (Vascular, V-HRF), and deposits of proteinaceous or lipid elements leaking from vessels (Exudative, E-HRF). Conclusions: HRF are emerging as valuable imaging biomarkers in retinal diseases. Four main types have been identified, with different morphological features, pathophysiological origin, and, therefore, different implications in the management of retinal diseases. Advances in imaging and computational analysis are promising for their incorporation into personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; biomarker; hyperreflective retinal foci; imaging; macular degeneration; macular diseases; macular edema; optical coherence tomography; retina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO International Programme on Chemical Safety Biomarkers and Risk Assessment: Concepts and Principles. 1993. [(accessed on 15 December 2024)]. Available online: http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc155.htm.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

