Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization in Waxy Sorghum Under Waxy Sorghum-Soybean Intercropping Systems
- PMID: 40364413
- PMCID: PMC12073204
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14091384
Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization in Waxy Sorghum Under Waxy Sorghum-Soybean Intercropping Systems
Abstract
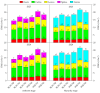
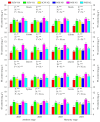
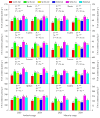
Waxy sorghum-soybean intercropping is a sustainable and intensive farming system in southwest China. However, there is limited knowledge about the effects of intercropped soybean combined with nitrogen application on nitrogen uptake and utilization in waxy sorghum. A two-year (2023 and 2024) field experiment was carried out using a randomized complete block design with three planting patterns and three nitrogen application rates to explore the responses of grain yield formation and nitrogen uptake, accumulation, transportation, metabolism physiology, and utilization of waxy sorghum for intercropped soybean combined with nitrogen application. Planting patterns included sole cropped waxy sorghum (SCW), sole cropped soybean (SCS), and waxy sorghum intercropped with soybean (WSI), and nitrogen application rates included zero nitrogen (N0), medium nitrogen (N1), and high nitrogen (N2). Results showed that the dry matter accumulation amount, nitrogen content, nitrogen accumulation amount, nitrogen transportation amount, nitrogen transportation rate, contribution rate of nitrogen transportation to grains, nitrogen metabolizing enzymes activities (including nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, glutamine synthetase, glutamate synthetase, glutamate dehydrogenase, and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase), and active substances contents (including soluble sugar, soluble protein, and free amino acid) in various organs of waxy sorghum among planting patterns and nitrogen application rates were in the order of WSI > SCW and N1 > N2 > N0, respectively. In addition, the nitrogen uptake efficiency, nitrogen agronomy efficiency, nitrogen apparent efficiency, nitrogen recovery efficiency, nitrogen partial factor productivity, and nitrogen contribution rate of waxy sorghum among planting patterns and nitrogen application rates were in the sequence of WSI > SCW and N1 > N2, respectively. The changes in above traits resulted in the WSI-N1 treatment obtaining the highest grain yield (6020.66 kg ha-1 in 2023 and 6159.81 kg ha-1 in 2024), grain weight per spike (65.22 g in 2023 and 64.51 g in 2024), 1000-grain weight (23.14 g in 2023 and 23.18 g in 2024) of waxy sorghum, and land equivalent ratio (1.41 in 2023 and 1.44 in 2024). Overall, waxy sorghum intercropped with soybean combined with medium nitrogen application (220 kg ha-1 for waxy sorghum and 18 kg ha-1 for soybean) can help enhance the nitrogen uptake and utilization of waxy sorghum by improving nitrogen metabolizing enzymes' activities and active substances' contents, thereby promoting its productivity.
Keywords: intercropping; nitrogen fertilizer; nitrogen use efficiency; waxy sorghum; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Changes in Nutrient Accumulation and Transportation of Waxy Sorghum in Waxy Sorghum-Soybean Intercropping Systems Under Different Row Ratio Configurations.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 22;13:921860. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.921860. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35937366 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizosphere soil properties of waxy sorghum under different row ratio configurations in waxy sorghum-soybean intercropping systems.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 6;18(7):e0288076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288076. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37410726 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of reduced N application rate on yield and nutrient uptake and utilization in maize-soybean relay strip intercropping system].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014 Feb;25(2):474-82. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 24830248 Chinese.
-
Assessing the impact of biochar and nitrogen application on yield, water-nitrogen use efficiency and quality of intercropped maize and soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 8;14:1171547. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1171547. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37223811 Free PMC article.
-
[Research advance in nitrogen metabolism of plant and its environmental regulation].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2004 Mar;15(3):511-6. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15228008 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Cowden R.J., Shah A.N., Lehmann L.M., Kiær L.P., Henriksen C.B., Ghaley B.B. Nitrogen fertilizer effects on pea-barley intercrop productivity compared to sole crops in Denmark. Sustainability. 2020;12:9335. doi: 10.3390/su12229335. - DOI
-
- Yahaya S.M., Mahmud A.A., Abdullahi M., Haruna A. Recent advances in the chemistry of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium as fertilizers in soil: A review. Pedosphere. 2023;33:385–406. doi: 10.1016/j.pedsph.2022.07.012. - DOI
-
- Anas M., Liao F., Verma K.K., Sarwar M.A., Mahmood A., Chen Z.L., Li Q., Zeng X.P., Liu Y., Li Y.R. Fate of nitrogen in agriculture and environment: Agronomic, eco-physiological and molecular approaches to improve nitrogen use efficiency. Bilo. Res. 2020;53:47. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00312-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashraf M., Shahzad S.M., Imtiaz M., Rizwan M.S. Salinity effects on nitrogen metabolism in plants—Focusing on the activities of nitrogen metabolizing enzymes: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2018;41:1065–1081. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2018.1431670. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

