Engineered Chitosan-Derived Nanocarrier for Efficient siRNA Delivery to Peripheral and Central Neurons
- PMID: 40364633
- PMCID: PMC12147987
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202500107
Engineered Chitosan-Derived Nanocarrier for Efficient siRNA Delivery to Peripheral and Central Neurons
Abstract
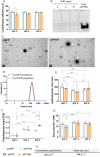
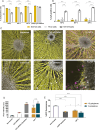
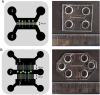
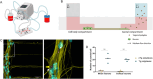
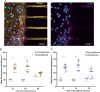
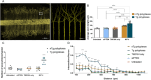
Gene therapy using small interfering RNA (siRNA) holds promise for treating neurological disorders by silencing specific genes, like the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene, which restricts axonal growth. Effective siRNA delivery to neurons, however, poses challenges due to premature nucleic acid degradation and unspecific delivery. Chitosan-based delivery systems, noted for their biocompatibility, face limitations such as low transfection efficiency and lack of neurotropism. Building on the previous successes with neuron-targeted DNA delivery using chitosan, a novel approach for siRNA delivery aimed at PTEN downregulation is proposed. This involves using thiolated trimethyl chitosan (TMCSH)-based siRNA nanoparticles functionalized with the neurotropic C-terminal fragment of the tetanus neurotoxin heavy chain (HC) for efficient delivery to peripheral and central neurons. These polyplexes demonstrate suitable physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and no adverse effects on neuronal electrophysiology. Diverse neuronal models, including 3D ex vivo cultures and microfluidics, confirm the polyplexes' efficiency and neurospecificity. HC-functionalization significantly enhances neuronal binding, and live cell imaging reveals fivefold faster retrograde transport along axons. Furthermore, siRNA delivery targeting PTEN promoted axonal outgrowth in embryonic cortical neurons. In conclusion, the proposed polyplexes represent a promising platform for neuronal siRNA delivery, offering potential for clinical translation and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: PTEN; chitosan; gene therapy; microfluidics; siRNA.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

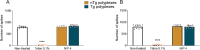
References
-
- Pena S. A., Iyengar R., Eshraghi R. S., Bencie N., Mittal J., Aljohani A., Mittal R., Eshraghi A. A., J. Drug Targeting 2020, 28, 111. - PubMed
-
- Ning K., Drepper C., Valori C. F., Ahsan M., Wyles M., Higginbottom A., Herrmann T., Shaw P., Azzouz M., Sendtner M., Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021.00472.CEECIND/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- 2024.01189.BD/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- SFRH/BD/137073/2018/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- PTDC/BTM-MAT/4156/2021/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- SFRH/BPD/122920/2016/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- PTDC/CTM-NAN/3547/2014/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT)
- 2248/19 1934/23/Israel Science Foundation
- 101086329/Israel Science Foundation
- PPBI-POCI-01-0145-FEDER-022122/Portuguese Platform of Bioimaging
- 101007804/H2020 European Research Council
- 3-17351/Ministry of Science and Technology, Israel
- 8-2175/Ministry of Science and Technology, Israel
- 9f51e2a4/European Cooperation in Science and Technology
- 10398/EMBO
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

