Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, biomarkers and immunotherapy
- PMID: 40364841
- PMCID: PMC12069044
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1577105
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, biomarkers and immunotherapy
Abstract
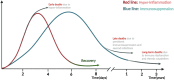
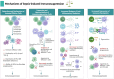
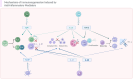
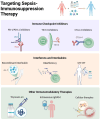
Sepsis, a life-threatening organ dysfunction resulting from a dysregulated host response to infection, initiates a complex immune response that varies over time, characterized by sustained excessive inflammation and immunosuppression. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression is now recognized as a major cause of septic death, and identifying effective strategies to counteract it poses a significant challenge. This immunosuppression results from the disruption of immune homeostasis, characterized by the abnormal death of immune effector cells, hyperproliferation of immune suppressor cells, release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and expression of immune checkpoints. Preclinical studies targeting immunosuppression, particularly with immune checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promise in reversing immunocyte dysfunctions and establishing host resistance to pathogens. Here, our review highlights the mechanisms of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and current diagnostic biomarkers, as well as immune-enhancing strategies evaluated in septic patients and therapeutics under investigation.
Keywords: biomarkers; immunology; immunosuppression; sepsis; therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Cai, Li and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment options.Mil Med Res. 2022 Oct 9;9(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00422-y. Mil Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36209190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy: A promising approach to reverse sepsis-induced immunosuppression.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:688-702. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27468649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Dec;13(12):862-74. doi: 10.1038/nri3552. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24232462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tim-3 pathway dysregulation and targeting in sepsis-induced immunosuppression.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 18;29(1):583. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02203-w. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39696711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential immunological mechanisms of sepsis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 8;15:1434688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434688. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39040114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An investigation of the relationship between sPD-1, sPD-L1 and severe pneumonia patients admitted to ICU and its clinical significance.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;12:1605653. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1605653. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40636377 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and topics on sepsis immunosuppression: a bibliometric and visual analysis of global research from 2004 to 2024.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 4;12:1615753. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1615753. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40832104 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

