Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, biomarkers and immunotherapy
- PMID: 40364841
- PMCID: PMC12069044
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1577105
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, biomarkers and immunotherapy
Abstract
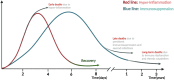
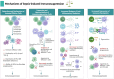
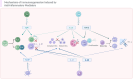
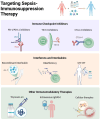
Sepsis, a life-threatening organ dysfunction resulting from a dysregulated host response to infection, initiates a complex immune response that varies over time, characterized by sustained excessive inflammation and immunosuppression. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression is now recognized as a major cause of septic death, and identifying effective strategies to counteract it poses a significant challenge. This immunosuppression results from the disruption of immune homeostasis, characterized by the abnormal death of immune effector cells, hyperproliferation of immune suppressor cells, release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and expression of immune checkpoints. Preclinical studies targeting immunosuppression, particularly with immune checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promise in reversing immunocyte dysfunctions and establishing host resistance to pathogens. Here, our review highlights the mechanisms of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and current diagnostic biomarkers, as well as immune-enhancing strategies evaluated in septic patients and therapeutics under investigation.
Keywords: biomarkers; immunology; immunosuppression; sepsis; therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Cai, Li and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

