A bivalent self-amplifying RNA vaccine against yellow fever and Zika viruses
- PMID: 40364846
- PMCID: PMC12069283
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569454
A bivalent self-amplifying RNA vaccine against yellow fever and Zika viruses
Abstract
Introduction: Yellow fever (YFV) and Zika (ZIKV) viruses cause significant morbidity and mortality, despite the existence of an approved YFV vaccine and the development of multiple ZIKV vaccine candidates to date. New technologies may improve access to vaccines against these pathogens. We previously described a nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC)-delivered self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) vaccine platform with excellent thermostability and immunogenicity, appropriate for prevention of tropical infectious diseases.
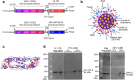
Methods: YFV and ZIKV prM-E antigen-expressing saRNA constructs were created using a TC-83 strain Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus-based replicon and complexed with NLC by simple mixing. Monovalent and bivalent vaccine formulations were injected intramuscularly into C57BL/6 mice and Syrian golden hamsters, and the magnitude, durability, and protective efficacy of the resulting immune responses were then characterized.
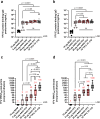
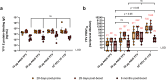
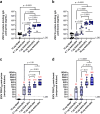
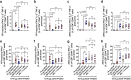
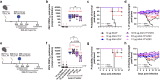
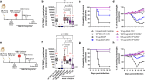
Results and discussion: Monovalent vaccines established durable neutralizing antibody responses to their respective flaviviral targets, with little evidence of cross-neutralization. Both vaccines additionally elicited robust antigen-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations. Notably, humoral responses to YFV saRNA-NLC vaccination were comparable to those in YF-17D-vaccinated animals. Bivalent formulations established humoral and cellular responses against both viral targets, commensurate to those established by monovalent vaccines, without evidence of saRNA interference or immune competition. Finally, both monovalent and bivalent vaccines completely protected mice and hamsters against lethal ZIKV and YFV challenge. We present a bivalent saRNA-NLC vaccine against YFV and ZIKV capable of inducing robust and efficacious neutralizing antibody and cellular immune responses against both viruses. These data support the development of other multivalent saRNA-based vaccines against infectious diseases.
Keywords: Zika virus; bivalent vaccine; flavivirus vaccine; nanostructured lipid carrier; self-amplifying RNA; yellow fever virus.
Copyright © 2025 Battisti, Ykema, Kasal, Jennewein, Beaver, Weight, Hanson, Singh, Bakken, Cross, Fusco, Archer, Reed, Gerhardt, Julander, Casper and Voigt.
Conflict of interest statement
AG and EV are co-inventors on U.S. patent application nos. PCT/US21/40388, “Co-lyophilized RNA and Nanostructured Lipid Carrier,” and 63/144,169, “A thermostable, flexible RNA vaccine delivery platform for pandemic response.” The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO expert committee on biological standardization. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. (2013) 979:1–366. Available at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/89156 (Accessed April 15, 2025). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

