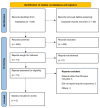
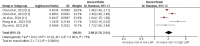Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40364881
- PMCID: PMC12070447
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.82166
Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains a significant global health challenge, necessitating innovative approaches for early risk stratification. This systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the prognostic value of the lactate-to-albumin ratio (LAR) in predicting all-cause mortality among MI patients. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, encompassing studies published until March 10, 2025. The meta-analysis included five studies involving 8,408 subjects with MI, all conducted in China between 2022 and 2024. Studies were selected based on predefined eligibility criteria, focusing on observational cohort and case-control designs, with LAR measured at admission and mortality outcomes reported. Pooled analysis revealed that patients with high LAR experienced approximately twice the risk of all-cause mortality compared to those with low LAR (hazard ratio: 2.08, 95% confidence interval: 1.70-2.54,p < 0.001). Significant heterogeneity was observed among studies (I2: 75%), which may be attributed to variations in patient populations and measurement methodologies. Despite limitations such as retrospective study designs and potential selection bias, the findings suggest LAR as a promising, accessible biomarker for early risk stratification in MI patients. Future research should focus on prospective studies to validate these results, establish standardized measurement protocols, and explore the underlying physiological mechanisms linking LAR to adverse outcomes.
Keywords: lactate to albumin ratio; mortality; myocardial infarction; prognostic biomarker; risk stratification.
Copyright © 2025, Ul Islam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between lactate/albumin ratio and 28-day all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with acute myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73788-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39389996 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-to-albumin ratio as a potential prognostic predictor in patients with cirrhosis and sepsis: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 14;25(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10601-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39953385 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and 28-days all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis: A retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 14;13:1076121. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1076121. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591285 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Elevated Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jun 4;16(6):e61647. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61647. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38966451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the lactate-to-albumin ratio to predict mortality in patients with sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Mar;26(5):1743-1752. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202203_28244. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35302224
References
-
- Impact of lactate/albumin ratio on prognostic outcomes in patients with concomitant heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Chen Y, Ba J, Peng C, Peng H, Li S, Lai W. Intern Emerg Med. 2024;19:1625–1636. - PubMed
-
- Serum albumin levels and inflammation. Sheinenzon A, Shehadeh M, Michelis R, Shaoul E, Ronen O. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;184:857–862. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous