Effects of dietary protein sources and levels on uric acid metabolism, renal function, and inflammatory responses in goslings
- PMID: 40365127
- PMCID: PMC12069410
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1587004
Effects of dietary protein sources and levels on uric acid metabolism, renal function, and inflammatory responses in goslings
Abstract
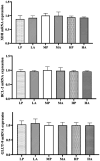
Dietary protein plays a crucial role in poultry nutrition, influencing nitrogen metabolism, renal function, and immune responses. This study investigated the effects of dietary protein source (plant-based vs. animal-based) and level (14.5, 18.5, and 22.5%) on serum biochemical parameters, renal metabolic markers, inflammatory cytokines, and gene expression in Jiangnan White goslings from day 1 to day 30 of age. A 2 × 3 factorial design was employed with 504 goslings randomly assigned to six groups, each comprising six replicates with 14 goslings per replicate. The results showed that dietary protein level significantly influenced serum uric acid (UA), creatinine (Cr), urea nitrogen (UN), and xanthine oxidase (XOD) activity, with goslings fed a high-protein diet (22.5%) exhibiting the highest levels (p < 0.05). Increased dietary protein also led to significantly elevated renal UA concentrations and XOD activity, particularly at 22 and 30 days (p < 0.05). In contrast, dietary protein source had limited influence on metabolic parameters, with only a transient difference in serum UA and Cr observed at 10 days of age (p < 0.05), and no significant effects on other serum or renal markers (p > 0.05). Additionally, renal inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-β) were significantly influenced by protein level, whereas XDH, BCL-2, and GLUT-9 mRNA expression remained unchanged (p > 0.05). No significant interactions between protein source and level were observed for most metabolic parameters, except for Cr and TNF-β. These findings suggest that total protein intake, rather than protein source, is the primary regulator of nitrogen metabolism and renal health in goslings. Optimization of protein levels is essential to balance growth performance and metabolic homeostasis.
Keywords: goslings; inflammatory cytokines; protein level; protein source; renal function; uric acid; xanthine oxidase.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Yang, Su, Li, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of betaine on growth performance, intestinal health, and immune response of goslings challenged with lipopolysaccharide.Poult Sci. 2022 Nov;101(11):102153. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102153. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 36179650 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of different dietary levels of sodium and chloride on performance and blood parameters in goslings (1-28 days of age).J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2020 Mar;104(2):507-516. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13273. Epub 2019 Dec 22. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31867808
-
The effects of dietary protein and fiber levels on growth performance, gout occurrence, intestinal microbial communities, and immunoregulation in the gut-kidney axis of goslings.Poult Sci. 2022 May;101(5):101780. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101780. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35325834 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Linking uric acid metabolism to diabetic complications.World J Diabetes. 2014 Dec 15;5(6):787-95. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i6.787. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 25512781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El Sebaei MG, Arafat N, El-Shafei RA, El-Adl MA, Farag A, Aziza AE, et al. . Biochemical and molecular investigation of oxidative stress associated with urolithiasis induced by increased dietary calcium or protein in chickens. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2021) 105:129–39. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13436, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chojnacka K, Mikula K, Izydorczyk G, Skrzypczak D, Witek-Krowiak A, Gersz A, et al. . Innovative high digestibility protein feed materials reducing environmental impact through improved nitrogen-use efficiency in sustainable agriculture. J Environ Manag. (2021) 291:112693. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112693, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous