Trends in Prevalence of Insulin Resistance Among Nondiabetic/Nonprediabetic Adolescents, 1999-2020
- PMID: 40365140
- PMCID: PMC12069839
- DOI: 10.1155/pedi/9982025
Trends in Prevalence of Insulin Resistance Among Nondiabetic/Nonprediabetic Adolescents, 1999-2020
Abstract
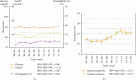
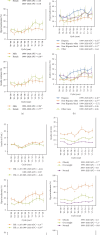
Purpose: Insulin resistance (IR)/hyperinsulinemia in young individuals is associated with the subsequent development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. To assess trends in the prevalence of IR/hyperinsulinemia among nondiabetic/nonprediabetic adolescents in the US from 1999 to 2020. Methods: A total of 6111 adolescents without diabetes and prediabetes were included from ten cycles of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) between 1999-2000 and 2017-2020. Hyperinsulinemia or IR was defined as fasting insulin or homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR] above the 75th percentile in all participants who underwent blood tests on fasting insulin, glucose, and hemoglobin A1c. Trends in prevalence rates were estimated using joinpoint regressions with heteroscedastic and uncorrelated errors. Results: The overall weighted median fasting insulin level, prevalence of hyperinsulinemia, and IR were 9.9 μU/ml [95% confidence interval (CI): 9.6, 10.1], 17.2% (95% CI: 15.7, 18.6), and 16.4% (95% CI: 15.2, 17.9), respectively. The estimated prevalence of hyperinsulinemia and HOMA-IR increased significantly from 15.2% (95% CI: 12.1, 18.9) and 14.0% (95% CI: 11.1, 17.8) in 1999-2000% to 21.5% (95% CI: 17.1, 26.3) and 20.4% (95% CI: 16.4, 25.6) in 2017-2020, respectively, with a 3.35% (95% CI: 1.74, 4.99) and 3.41% (95% CI: 1.72, 5.12) relative increase per 2-year survey cycle, respectively (p for trend <0.05). Substantial increases were observed in the subgroups of girls, Hispanic, non-Hispanic white, and overweight adolescents. Conclusions: The prevalence of hyperinsulinemia/IR increased substantially among US nondiabetic/nonprediabetic adolescents over the last two decades. Early detection and effective interventions are in dire need to reverse the rising tide.
Keywords: adolescents; hyperinsulinemia; insulin resistance; prevalence; trends.
Copyright © 2025 Dongying Zhao et al. Pediatric Diabetes published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in hyperinsulinemia among nondiabetic adults in the U.S.Diabetes Care. 2006 Nov;29(11):2396-402. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0289. Diabetes Care. 2006. PMID: 17065674
-
Trends in Hyperinsulinemia and Insulin Resistance Among Nondiabetic US Adults, NHANES, 1999-2018.J Clin Med. 2025 May 6;14(9):3215. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093215. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364246 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of pre-diabetes and its association with clustering of cardiometabolic risk factors and hyperinsulinemia among U.S. adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006.Diabetes Care. 2009 Feb;32(2):342-7. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1128. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 18957533 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance among nondiabetic US adults, NHANES, 1999-2018.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 18:rs.3.rs-5279795. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5279795/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: J Clin Med. 2025 May 06;14(9):3215. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093215. PMID: 39606490 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Prevalence of Prediabetes Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States, 2005-2016.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Feb 1;174(2):e194498. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.4498. Epub 2020 Feb 3. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31790544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weyer C., Hanson R. L., Tataranni P. A., Bogardus C., Pratley R. E. A High Fasting Plasma Insulin Concentration Predicts Type 2 Diabetes Independent of Insulin Resistance: Evidence for a Pathogenic Role of Relative Hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes . 2000;49(12):2094–2101. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.12.2094. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sinaiko A. R., Steinberger J., Moran A., Hong C. P., Prineas R. J., Jacobs D. R. Influence of Insulin Resistance and Body Mass Index at Age 13 on Systolic Blood Pressure, Triglycerides, and High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol at Age 19. Hypertension . 2006;48(4):730–736. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000237863.24000.50. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J., Schwarz P. E. Preventing Diabetes: Early Versus Late Preventive Interventions. Diabetes Care . 2016;39(Suppl 2):S115–120. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

