Recognizing Kounis Syndrome, the Unusual Possible Culprit of Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Rare Case Report
- PMID: 40365145
- PMCID: PMC12068912
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1743564
Recognizing Kounis Syndrome, the Unusual Possible Culprit of Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Rare Case Report
Abstract
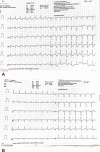
Kounis syndrome encompasses acute coronary syndrome features associated with severe vasospasm of the coronary artery. It is related to allergic anaphylactic reaction triggered by the release of inflammatory cells and mediators. This entity, however, is often not properly diagnosed. In this report, we aimed to discuss a case of Kounis syndrome mimicking acute coronary syndrome. We presented a 58-year-old man with dyspnea, chest pain, dizziness, and itchiness 30 minutes following sodium diclofenac ingestion. His physical examination was remarkable for shock with hypoxia and features of anaphylactic reaction. An urgent electrocardiogram was obtained, manifesting deep ST-segment depression in anterolateral leads with ST elevation of aVR, which hinted a severe three-vessel disease or left main disease. Allergic acute coronary syndrome was suspected. Thus, the patient was managed with fluid resuscitation, epinephrine, and corticosteroid injection along with acute coronary syndrome treatment algorithm with a favorable clinical response. One-hour serial ECG showed complete resolution of ST depression with aVR normalization. This pointed to possible acute coronary spasm. No further coronary intervention was performed, the patient was discharged after 2 days in good condition and planned for further cardiac evaluation during follow-up. Kounis syndrome is an intriguing process caused by the presence of two disease entities that must be treated simultaneously. The difficulty in treating this condition stems from the fact that treating one of both entities may aggravate the other. Thus, a comprehensive approach and health education are strongly advised to ensure that this condition does not reoccur in the future.
Keywords: Kounis syndrome; acute coronary syndrome; anaphylaxis reaction; case report.
International College of Angiology. This article is published by Thieme.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insight into the Time Course of Type III Kounis Syndrome: A Case Report.J Emerg Med. 2020 Aug;59(2):e65-e68. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2020.04.054. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32536494
-
Kounis syndrome type I induced by an intramuscular injection of diclofenac: A literature review based on a case report.Clin Case Rep. 2024 Jul 21;12(7):e9198. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.9198. eCollection 2024 Jul. Clin Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39040609 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory cardiac arrest caused by type I Kounis syndrome treated with adrenaline and nicorandil: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 11;102(32):e34535. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034535. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37565887 Free PMC article.
-
Kounis syndrome secondary to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid administration: a case report and review of literature.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Mar 26;8:97. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1072-5. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 25889048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute coronary syndrome secondary to allergic coronary vasospasm (Kounis Syndrome): a case series, follow-up and literature review.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Feb 27;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0781-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29486712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

