Gender-specific association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40365228
- PMCID: PMC12069050
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1541961
Gender-specific association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR), one of the most common microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus (DM), remains to be a major driver of vision loss worldwide. Vitamin D has been reported to be involved in DR pathogenesis, but results have been inconsistent. We aimed to explore the relationship between blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D, 25(OH)D, level and the risk of DR in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
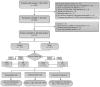
Methods: A total of 535 adults with T2DM from our department were included. Demographic information, biochemical data, 25(OH)D, and sex hormones were collected. Fundus photography was performed to determine the presence of DR. Participants were grouped into the DR group and the non-DR (NDR) group according to the fundus examinations and four groups based on serum 25(OH)D levels as follows: normal, insufficient, deficient, and severely deficient. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association between 25(OH)D and risk of DR.
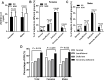
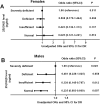
Results: Males but not females with DR had significantly decreased levels of 25(OH)D (16.4 ± 5.6 ng/ml vs. 21.0 ± 5.0 ng/ml, P = 0.001) and increased proportion of severe 25(OH)D deficiency (14.8% vs. 6.7%, P = 0.022) compared to those without DR. Likewise, there was a gradually increasing percentage of DR with the reduction of 25(OH)D levels only in males (35.7%, 44.4%, 53.2%, 70.3%, P = 0.022). Intriguingly, total testosterone (TT) levels decreased markedly in males with DR (12.9 ± 5.2 nmol/L vs. 14.2 ± 5.5 nmol/L, P = 0.035) compared to their counterparts and correlated positively with 25(OH)D (β = 0.161, P = 0.007), which did not occur in females. After multivariate adjustment, we observed a significant inverse association between serum 25(OH)D and the occurrence of DR in males, showing that the adjusted ORs (AORs) and 95% confidence interval for DR were 0.233 (0.070-0.779) in the normal group, 0.280 (0.103-0.756) in the insufficient group, and 0.477 (0.196-1.164) in the deficiency group with the severely deficient group as a reference (P-trend = 0.003). However, such a significant association was not observed in females (P-trend = 0.137).
Conclusion: We concluded a gender-specific relationship between serum 25(OH)D and the incidence of DR in T2DM, supported by a significant inverse association between serum 25(OH)D and DR only in males, which could be mediated by a marked reduction in TT levels.
Keywords: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; diabetic retinopathy; gender-specific difference; total testosterone; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 He, Kang, Mei, Zhou, Yin and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin D Deficiency Is Significantly Associated with Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study.Nutrients. 2021 Dec 25;14(1):84. doi: 10.3390/nu14010084. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 35010958 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum vitamin D levels and diabetic retinopathy in Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018 May;139:308-313. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.040. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 29518485
-
Relationship between vitamin D status and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nutr Res. 2016 Feb;36(2):117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 26826427
-
The relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and a meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Nov;98(48):e18118. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018118. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31770239 Free PMC article.
-
The association between fibroblast growth factor 21 with diabetes retinopathy among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 13;12:e18308. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18308. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39687000 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

