Targeting neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer progression and metastasis
- PMID: 40365275
- PMCID: PMC12068306
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.111096
Targeting neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer progression and metastasis
Abstract
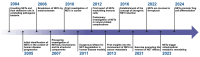
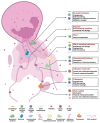
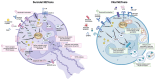
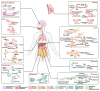
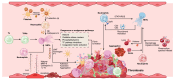
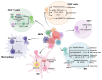
Neutrophils serve as pivotal effectors and regulators of the intricate immune system. Their contributions are indispensable, encompassing the obliteration of pathogens and a significant role in both cancer initiation and progression. Conversely, malignancies profoundly affect neutrophil activity, maturation, and lifespans. Cancer cells manipulate their biology to enhance or suppress the key functions of neutrophils. This manipulation is one of the most remarkable defensive mechanisms used by neutrophils, including the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). NETs are filamentous structures comprising DNA, histones, and proteins derived from cytotoxic granules. In this review, we discuss the bidirectional interplay in which cancer elicits NET formation, and NETs concurrently facilitate cancer progression. Here, we discuss how vascular dysfunction and thrombosis induced by neutrophils and NETs contribute to an elevated risk of mortality from cardiovascular complications in patients with cancer. Ultimately, we propose a series of therapeutic strategies that hold promise for effectively targeting NETs in clinical settings.
Keywords: cancer progression; metastasis; neutrophil extracellular traps; therapeutic targets; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NETworking with cancer: The bidirectional interplay between cancer and neutrophil extracellular traps.Cancer Cell. 2023 Mar 13;41(3):505-526. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.001. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Cancer Cell. 2023. PMID: 36827980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Tumor Progression and Metastasis.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 16;11:1749. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01749. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps in tumor progression of gynecologic cancers.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 1;15:1421889. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421889. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39555072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Trapping Role in Cancer, Metastases, and Cancer-Related Thrombosis: a Narrative Review of the Current Evidence Base.Curr Oncol Rep. 2021 Aug 3;23(10):118. doi: 10.1007/s11912-021-01103-0. Curr Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34342735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7260. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147260. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophils and NETs in Pathophysiology and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7098. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157098. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

