Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by inhibiting Nrf2/Keap1 complex formation
- PMID: 40365306
- PMCID: PMC12069325
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542296
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by inhibiting Nrf2/Keap1 complex formation
Abstract
Introduction: Drug-induced cardiotoxicity (DICT), defined as myocardial injury caused by direct or indirect toxicity of therapeutic agents, disrupts cardiovascular homeostasis, underscoring the urgent need for preventive strategies in clinical practice. Doxorubicin (DOX), a clinically established anthracycline chemotherapeutic, induces dose-dependent cardiotoxicity driven by reactive oxygen species overproduction. Notably, Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP), a bioactive phytochemical derived from celery, has shown potential in mitigating DOX-induced cardiomyopathy via its antioxidant activity. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the protective effects of NBP on DOX-induced cardiomyopathy, with a focus on elucidating the underlying mechanisms.
Method: We developed both in vivo and in vitro models of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. For the animal model, male C57BL/6 mice were administered with DOX (4 mg/kg, i.p.) once a week for 3 weeks. For the cell model, H9C2 myoblasts were exposed to 1 μM DOX for at least 6 h to establish acute cardiotoxicity.
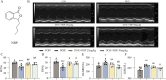
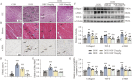
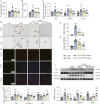
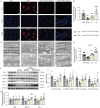
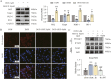
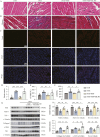
Results: Our results demonstrate that NBP significantly improves cardiac function, as evidenced by approximately 10% increase in cardiac functional parameters (ejection fraction and left ventricular shortening fraction). Besides, NBP exerts favorable effects on cardiac inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, and mitochondrial damage both in vivo and in vitro. Further mechanistic investigations revealed that NBP blocks the interaction between Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1) and Nrf2, thereby preventing the formation of the Nrf2/Keap1 complex.
Discussion: This study indicate that NBP alleviates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting Nrf2/Keap1 complex formation, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for DICT and suggest that Nrf2/Keap1 may be a potential therapeutic target for the management of this condition.
Keywords: C57BL/6 mice; Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP); doxorubicin (DOX); drug-induced cardiotoxicity (DICT); kelch-like ECH associated protein-1 (Keap1); nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2).
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Fang, Zhao, Lin, Tong, Xiang, Ran, Wang, Li, Chen and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DL-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 6;10(5):e27644. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27644. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38486757 Free PMC article.
-
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting the binding of Nrf2/Keap1.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025 Sep;502:117424. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2025.117424. Epub 2025 May 31. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40456322
-
Disruption of the Keap1/Nrf2-Antioxidant Response System After Chronic Doxorubicin Exposure In Vivo.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020 Dec;20(6):557-570. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09581-7. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32500386
-
Cardiac sirtuin1 deficiency exacerbates ferroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury through the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 May 25;377:110469. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110469. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 37030624
-
Erianin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jun;141:156684. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156684. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40215822
Cited by
-
Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Update.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 May 30;12(6):207. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12060207. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40558642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boddicker N. J., Larson M. C., Castellino A., Herrmann J., Inwards D. J., Thanarajasingam G., et al. (2021). Anthracycline treatment, cardiovascular risk factors and the cumulative incidence of cardiovascular disease in a cohort of newly diagnosed lymphoma patients from the modern treatment era. Am. J. Hematol. 96 (8), 979–988. 10.1002/ajh.26230 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

