Successful Pregnancy Management of a Woman With Severe Methylmalonic Acidemia
- PMID: 40365323
- PMCID: PMC12069855
- DOI: 10.1002/jmd2.70009
Successful Pregnancy Management of a Woman With Severe Methylmalonic Acidemia
Abstract
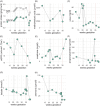
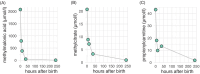
Isolated methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) is a rare, genetically heterogeneous group of metabolic disorders resulting from a deficiency of the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MMUT), defects in the metabolism of its cofactor, adenosylcobalamin, or deficiency of the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase. With improved awareness, earlier diagnosis, and advances in care, women with MMA are increasingly reaching childbearing age, and successful pregnancies have been documented in patients with milder forms of the disease. This report details, for the first time, the management and outcomes of pregnancy in a woman with severe mut0 deficiency and concomitant advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring initiation of hemodialysis at 21 weeks' gestation. At 20 weeks, fetal ultrasound revealed fetal growth restriction (FGR), necessitating close monitoring and dietary adjustments to meet the patient's increased nutritional needs. Despite these challenges, she remained metabolically stable until delivery. At 35 weeks, she delivered a 1.64 kg male SGA newborn via cesarean section. The newborn presented with mild retrognathia, a soft palate cleft, mild hypospadias, mild ventriculomegaly, and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and cerebellum without the need for immediate intervention. The mother experienced a mild metabolic decompensation on the fifth postpartum day, which was promptly managed by additional renal replacement therapy. At 3 months postpartum, both mother and child were doing well, with no further metabolic complications observed. This case report demonstrates that pregnancy in patients with severe mut0 deficiency is challenging and requires a close interdisciplinary management but can be carried out with a favorable outcome.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; interdisciplinary management; pregnancy; severe methylmalonic acidemia.
© 2025 The Author(s). JIMD Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of SSIEM.
Conflict of interest statement
G.E. reports grants and personal fees from Bioporto, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Langendonk J. G., Roos J. C. P., Angus L., et al., “A Series of Pregnancies in Women With Inherited Metabolic Disease,” Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 35 (2012): 419–424. - PubMed
-
- Wasserstein M. P., Gaddipati S., Snyderman S. E., Eddleman K., Desnick R. J., and Sansaricq C., “Successful Pregnancy in Severe Methylmalonic Acidaemia,” Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 22 (1999): 788–794. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

