A Systematic Review of Yoga Interventions on the Mental Health of Nursing Professionals and Students
- PMID: 40365361
- PMCID: PMC12068460
- DOI: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_195_24
A Systematic Review of Yoga Interventions on the Mental Health of Nursing Professionals and Students
Abstract
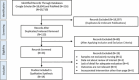
This systematic review aimed to evaluate the impact of yoga interventions on preventing and alleviating mental health issues, including stress, anxiety, burnout, depression, and other related factors among nursing professionals and students. The review adhered to the PRISMA guidelines and was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024512366). A comprehensive literature search was conducted in Google Scholar and PubMed using keywords such as "nursing students," "nursing professionals," "yoga interventions," and "mental health." Eligible studies were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from 1st January 2014 to 31st December 2024, involving nursing population and yoga-based interventions targeting mental health outcomes. The risk of bias was assessed using the CASP tool. The search identified 14 RCTs (967 participants, predominantly female, age range - 18 to 69 years) that met the eligibility criteria. The yoga intervention varied in duration (10 minutes to 1 hour per session), frequency (once to five times weekly), and protocols (Laughter yoga being the most common). Mental health outcomes such as stress, anxiety, burnout, mindfulness, depression, quality of sleep, and life satisfaction were assessed. Most studies reported significant improvements in these outcomes in the yoga intervention groups compared to control groups. Nine studies showed a significant stress reduction, and 3 studies found a decrease in anxiety. No adverse effects were reported, and dropout rates varied between 0% to 52.1%. Yoga was found to be effective in improving mental health and well-being among nursing professionals and students. Yoga mainly reduced stress, anxiety, burnout, and depression, suggesting its potential as a low-cost, accessible intervention for mental health management in this population. Future studies should focus on refining protocols and exploring long-term effects to establish yoga as an integral part of mental health care for nursing professionals and students.
Keywords: Anxiety; burnout; depression; mental health; nursing professionals; nursing students; randomized controlled trial; stress; systematic review; yoga.
Copyright: © 2025 International Journal of Yoga.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness of mindfulness based programs in reducing stress experienced by nurses in adult hospital settings: a systematic review of quantitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):21-9. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2380. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571279
-
The impact of laughter yoga as a NIC on health parameters in nurses and nursing students: a systematic review.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Oct 29;24(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04663-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39472871 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of tele-yoga on burnout, mental health and immune markers of health care workers on COVID-19 duty: An open-label parallel group pilot randomized controlled trial.Complement Ther Med. 2024 Dec;87:103109. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2024.103109. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Complement Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39521190 Clinical Trial.
-
Mobile apps to reduce depressive symptoms and alcohol use in youth: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 26;20(2):e1398. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1398. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38680950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Yoga on cognition and mental health among elderly: A systematic review.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Aug;52:102421. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102421. Epub 2020 May 19. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32951703
References
-
- Anand S, Fan V. World Health Organization. The Health Workforce in India. 2016
-
- Wang P, Tang YL, Chen Y, He Y, Li L, Han X, et al. Mental health status of mental health nurses in China: Results from a national survey. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2023;30:547–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous