Unveiling Therapeutic Potential of Yoga Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PCOS: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40365366
- PMCID: PMC12068466
- DOI: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_212_24
Unveiling Therapeutic Potential of Yoga Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PCOS: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Hormonal imbalance, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and oxidative stress (OS) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and its associated clinical features. A sedentary lifestyle, exposure to air pollutants, prenatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, processed and nutritionally depleted food, rich in trans fats, salts, and sugars, and high BMI specifically in visceral adiposity induce OS. OS damages the mitochondrial DNA, lipids, and proteins that impair mitochondrial function. Sequentially, dysfunctional mitochondria produce more reactive oxygen species that aggravate the OS. Mitochondria is pivotal for ovarian cell functioning for instance steroidogenesis, ovarian follicle development, and energy metabolism. Dysfunctional mitochondria can alter the ovarian follicle functioning leading to ovulatory dysfunction and infertility in PCOS.
Aims and objectives: This study is designed to investigate the effect of 12-week yoga practice on endocrine parameters, OS, and mitochondrial health, comparing outcomes in yoga and non-yoga groups.
Material and methods: A total of 75 participants, 32 PCOS females who completed yoga intervention in the yoga group and 29 in the nonyoga group. Hormonal levels were assessed through an immunoassay, while mitochondrial health markers, such as mtDNA copy number (mtDNA CN), reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation were measured through quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), chemiluminescence, and ELISA respectively. Gene expression related to mitochondrial integrity, respiratory chain, and inflammation was analyzed via reverse transcription qPCR. Additionally, depression severity was also assessed using beck depression inventory II.
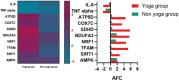
Result: The Yoga group showed a significant increase in mtDNA-CN and upregulation of transcripts responsible for maintaining mitochondrial integrity and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. In addition, the post-yoga group shows a reduction in, lipid peroxidation, inflammatory, OS markers, and an improvement in telomere length.
Conclusion: Yoga positively affects hormonal balance, mitochondrial health, OS, and inflammation in women with PCOS. It also alleviates depression symptoms, highlighting yoga as an effective adjunct therapy for managing PCOS. Regular yoga practice could prevent, delay, and help in managing PCOS symptoms.
Keywords: Inflammation; PCOS; micronanoplastics; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; plastics; yoga.
Copyright: © 2025 International Journal of Yoga.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
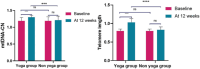
Similar articles
-
Yoga improves mitochondrial health and reduces severity of autoimmune inflammatory arthritis: A randomized controlled trial.Mitochondrion. 2021 May;58:147-159. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.03.004. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Mitochondrion. 2021. PMID: 33741520 Clinical Trial.
-
Yoga Intervention Improves the Metabolic Parameters and Quality of Life among Infertile Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Indian Population.Int J Yoga. 2023 May-Aug;16(2):98-105. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_88_23. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Int J Yoga. 2023. PMID: 38204771 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction of granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 28;10:1193749. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1193749. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37448805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of nitric oxide and oxidative stress in typical ovulatory women and in the pathogenesis of ovulatory dysfunction in PCOS.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023 Nov 23;21(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12958-023-01159-6. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37996893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Contribution of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations and Dysfunction in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Supported by Secondary Database Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 29;26(3):1172. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031172. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS consensus workshop group Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Hum Reprod. 2004;19:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Bhandary P, Shetty PK, Manjeera L, Patil P. Hormonal, genetic, epigenetic and environmental aspects of polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gene Rep. 2022;29:101698.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
