Deep learning and radiomics-driven algorithm for automated identification of May-Thurner syndrome in Iliac CTV imaging
- PMID: 40365495
- PMCID: PMC12069258
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1526144
Deep learning and radiomics-driven algorithm for automated identification of May-Thurner syndrome in Iliac CTV imaging
Abstract
Objective: This research aimed to create a dataset of Iliac CTV scans for automated May-Thurner syndrome (MTS) detection using deep learning and radiomics. In addition, it sought to establish an automated segmentation model for Iliac Vein CTV scans and construct a radiomic signature for MTS diagnosis.
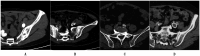
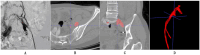
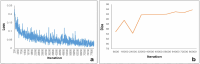
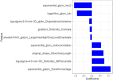
Methods: We collected a dataset of 490 cases meeting specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, anonymized to comply with HIPAA regulations. Iliac Vein CTV scans were prepared with contrast agent administration, followed by image acquisition and evaluation. A deep learning-based segmentation model, UPerNet, was employed using 10-fold cross-validation. Radiomic features were extracted from the scans and used to construct a diagnostic radiomic signature. Statistical analysis, including Dice values and ROC analysis, was conducted to evaluate segmentation and diagnostic performance.
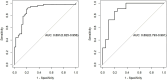
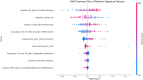
Results: The dataset consisted of 201 positive cases of MTS and 289 negative cases. The UPerNet segmentation model exhibited remarkable accuracy in identifying MTS regions. A Dice coefficient of 0.925 (95% confidence interval: 0.875-0.961) was observed, indicating the precision and reliability of our segmentation model. Radiomic analysis produced a diagnostic radiomic signature with significant clinical potential. ROC analysis demonstrated promising results, underscoring the efficacy of the developed model in distinguishing MTS cases. The radiomic signature demonstrated strong diagnostic capabilities for MTS. Within the training dataset, it attained a notable area under the curve (AUC) of 0.891, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.825 to 0.956, showcasing its effectiveness. This diagnostic capability extended to the validation dataset, where the AUC remained strong at 0.892 (95% confidence interval: 0.793-0.991). These results highlight the accuracy of our segmentation model and the diagnostic value of our radiomic signature in identifying MTS cases.
Conclusion: This study presents a comprehensive approach to automate MTS detection from Iliac CTV scans, combining deep learning and radiomics. The results suggest the potential clinical utility of the developed model in diagnosing MTS, offering a non-invasive and efficient alternative to traditional methods.
Keywords: Computed Tomography Venography; Convolutional Neural Networks; May-Thurner syndrome; deep learning; iliac vein compression.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Li, Zheng and Qiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of deep learning and radiomic signatures for overall survival prediction in recurrent high-grade glioma treated with immunotherapy.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jan 21;25(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00818-0. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39838503 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional computed tomography venography reconstruction facilitates identification of atypical radiologic features of May-Thurner syndrome.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021 Jul;9(4):946-953. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.11.014. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021. PMID: 33248296
-
Multimodal data deep learning method for predicting symptomatic pneumonitis caused by lung cancer radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1492399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1492399. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39845959 Free PMC article.
-
Automated MRI liver segmentation for anatomical segmentation, liver volumetry, and the extraction of radiomics.Eur Radiol. 2024 Aug;34(8):5056-5065. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10495-5. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38217704 Free PMC article.
-
Iliac vein compression syndrome: Clinical, imaging and pathologic findings.World J Radiol. 2015 Nov 28;7(11):375-81. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.375. World J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26644823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nagarsheth K, Fitzpatrick S, Castillo L, Abdulrahman L, Dunlap E. Surgical anteriorization of the left common iliac vein results in improved venous outflow and quality of life for May-Thurner syndrome. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. (2024) 10:101495. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2024.101495, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

