Diagnostic Accuracy of Serum P16ink4A and FOX-P3 Concentrations for Detection of Cervical Lesions Among Women Attending a Cervical Cancer Clinic in Western Uganda: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 40365511
- PMCID: PMC12074841
- DOI: 10.1155/ancp/1931921
Diagnostic Accuracy of Serum P16ink4A and FOX-P3 Concentrations for Detection of Cervical Lesions Among Women Attending a Cervical Cancer Clinic in Western Uganda: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
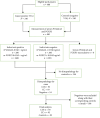
Introduction: Expression of P16ink4A and FOXP3 is correlated with the grades of cervical lesions. In this study, we determined the diagnostic accuracy of serum P16ink4A and FOXP3 concentrations for detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer (CC) in a rural setting in Southwestern Uganda. Material and Methods: CIN and CC cases (93 each before treatment), and 93 controls were identified. Clinical and demographic data were documented before quantifying serum P16ink4A and FOXP3 concentrations using quantitative ELISA kits. Cases were confirmed by cytology and/or histology. We employed descriptive statistics, cross-tabulation, and receiver operating curves (ROC) using statistical software for data science (STATA) 17. p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results: Serum FOXP3 concentration of 0.0545 ng/mL < showed moderate sensitivity (32.22% and 57.78%) for detection of CIN and CC from healthy controls, respectively. It also showed a moderately high specificity of 68.89% for detection of both CIN and CC from healthy controls (AUC-0.6014 and 0.7679, respectively). Serum P16ink4A concentration of 0.946 ng/mL < showed moderate sensitivities (50.00% and 60.00%) and specificities (56.67% and 55.56%) for the detection of CIN and CC from healthy controls, respectively (AUC-0.6085 and 0.7592, respectively). A combination of elevated serum FOXP3 and P16ink4A showed very low sensitivities of 18.89% in detecting CIN from healthy controls and 33.33% for detecting CC from healthy controls. This combination showed high specificity of 83.33% in detecting both CIN and CC from healthy controls (AUC-0.5992 and 0.7642, respectively). Conclusion: Although serum P16ink4A and FOXP3 concentrations showed moderate accuracy, their combination was more specific than sensitive. This combination has a high potential to be applied for diagnosis rather than screening for cervical lesions, at least in the Ugandan population. Combinations of P16ink4A and FOXP3 with other biomarkers could improve diagnostic accuracies. Additionally, studies could be conducted to assess the performance of these biomarkers in the detection of cervical lesions in specific populations, say Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-positive and HIV-negative populations.
Keywords: FOXP3; P16ink4A; accuracy; cervical cancer; cervical intraepithelial lesions; serum.
Copyright © 2025 Frank Ssedyabane et al. Analytical Cellular Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wanyenze R. K., Matovu J. K., Bouskill K., et al. Social Network-Based Group Intervention to Promote Uptake of Cervical Cancer Screening in Uganda: Study Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Pilot and Feasibility Studies . 2022;8(1):p. 247. doi: 10.1186/s40814-022-01211-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nelson J. A., Francis S. A., Liverpool J., Soogun S., Mofammere N. Healers in a Non-Traditional Role; a Focus Group Study of Sangoma’s Knowledge of and Attitudes to Cervical Cancer Prevention and Screening in Johannesburg, South Africa. Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare . 2010;1(4):195–196. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2010.07.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

