HBV core protein enhances WDR46 stabilization to upregulate NUSAP1 and promote HCC progression
- PMID: 40366140
- PMCID: PMC12055171
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000680
HBV core protein enhances WDR46 stabilization to upregulate NUSAP1 and promote HCC progression
Abstract
Background: The HBV core protein (HBC) is crucial for the progression of HCC. WD repeat-containing (WDR) 46 (WDR46) is implicated in the development of different tumors. Nevertheless, whether WDR46 is controlled by HBC to drive hepatocarcinogenesis remains unclear.
Methods: Different HCC cohorts, immunohistochemical staining, and bioinformatics analysis were utilized to estimate the clinical correlation between WDR46 and HBV-associated HCC. Western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and oncology functional assays were performed to evaluate the effect of HBC on WDR46 in upregulating nucleolar spindle-associated protein 1 (NUSAP1), the influence of WDR46 on HBC-mediated HCC cell biological functions, and the mechanisms of WDR46 upregulation mediated by HBC to increase NUSAP1.
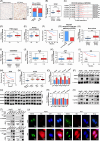
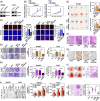
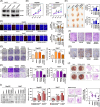
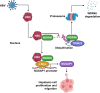
Results: WDR46 expression was elevated in HBV-related HCC in a HBC-dependent manner. Overexpression of WDR46 is closely linked to severe prognosis of tumors. Functionally, WDR46 contributes to HBC-induced cell growth and migration in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, HBC enhanced WDR46 protein stabilization by hampering the interaction between WDR46 and TRIM25, thereby decreasing WDR46 ubiquitination. NUSAP1, a DNA replication-related molecule, is a vital downstream target of WDR46. Relying on WDR46, HBC promoted NUSAP1 upregulation to modulate the biological functions of HBC in HCC cells. Importantly, HBC enhanced the interaction between WDR46 and the transcription factor c-Myc to facilitate c-Myc recruitment to the NUSAP1 promoter, leading to the increase of NUSAP1 transcription.
Conclusions: Our comprehensive data provides new insights into the mechanisms responsible for HBC-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. WDR46 and its downstream molecule, NUSAP1, may act as novel therapeutic targets for HBV-related tumors.
Keywords: HBV core protein; NUSAP1; TRIM25; WDR46; c-Myc.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures




References
-
- Kong F, Li N, Tu T, Tao Y, Bi Y, Yuan D, et al. . Hepatitis B virus core protein promotes the expression of neuraminidase 1 to facilitate hepatocarcinogenesis. Lab Invest. 2020;100:1602–1617. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

