Development and validation of a blocking ELISA for measurement of rabies virus neutralizing antibody
- PMID: 40366189
- PMCID: PMC12153311
- DOI: 10.1128/jcm.02049-24
Development and validation of a blocking ELISA for measurement of rabies virus neutralizing antibody
Abstract
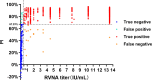
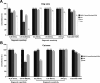
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an effective approach for monitoring herd immunity of animals against rabies but not recommended to detect neutralizing antibody response of individual animals in the framework of international travel since its insufficient agreement with the globally recognized rabies virus (RABV) neutralizing tests. In this study, a blocking ELISA to specifically detect anti-RABV neutralizing antibody was developed using the purified RABV glycoprotein (G) expressed in HEK293T cells as coating antigen, and a labeled anti-G neutralizing monoclonal antibody as the blocking antibody. The overall agreement between the blocking ELISA and fluorescent antibody virus neutralization test in detection of clinical serum samples (dogs = 658; cats = 508) was 97.43% (1,136/1,166), with a diagnostic specificity of 95.63% (219/229) and a diagnostic sensitivity of 97.87% (917/937). Further comparison with the commercial ELISA kits and inter-laboratory validation showed that the blocking ELISA had excellent specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. In conclusion, the developed method is a potential tool as an alternative to the virus neutralization test for the detection of canine and feline rabies neutralization antibodies following vaccination.IMPORTANCEThis study establishes a blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detecting rabies neutralizing antibodies in dogs and cats, demonstrating high sensitivity, specificity, and no cross-reactivity. This method provides a reliable alternative to conventional neutralization assays, facilitating efficient large-scale rabies vaccination assessment, and thereby strengthening global rabies control efforts.
Keywords: blocking ELISA; monoclonal antibody; neutralizing antibody detection; rabies virus glycoprotein; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
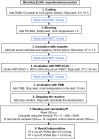
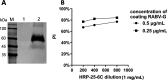
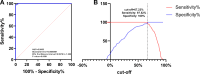
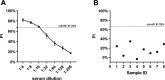
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2013. World Health Organization technical report series. WHO expert consultation on rabies. Second report, Vol. 982, p 1–139. Vol. 982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

