Pre-Formulation Studies of Lipid-Based Formulation Approach for a Poorly Water-Soluble Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II Model Drug: Bosentan
- PMID: 40366240
- PMCID: PMC12080292
- DOI: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2025.48840
Pre-Formulation Studies of Lipid-Based Formulation Approach for a Poorly Water-Soluble Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II Model Drug: Bosentan
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to perform pre-formulation studies, formulation development, and formulation optimization for self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS), a lipid-based formulation approach to improve the low solubility of bosentan monohydrate (BOS).
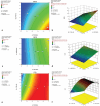
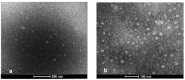
Materials and methods: Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were created for pre-formulation studies and formulation design for SNEDDS. The SNEDDS was optimized with BBD. The optimized BOS-loaded SNEDDS formulation was characterized by droplet size (DS), polydispersity index (PDI), dispersibility, an efficiency test of self-nanoemulsification, % transmittance, turbidity, robustness, and the effects of pH, viscosity, and thermodynamic and long-term stability studies. The in vitro dissolution studies were performed in distilled water containing 1% sodium lauryl sulfate, which is a Food and Drug Administration-recommended medium, and in biorelevant media. Ex vivo studies were conducted in biorelevant media.
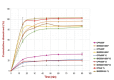
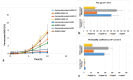
Results: The optimum BOS-loaded SNEDDS had a DS of 16.76 nm and PDI of 0.200. The characterization studies satisfied SNEDDS requirements (does not deteriorate when diluted at different pHs; resistant to thermodynamic changes; self-emulsifying within 1 minute; Grade A; and transparent) for both blank and BOS-loaded SNEDDS. In long-term stability studies, it was found to be stable for six months. When in vitro dissolution was compared to the performance of the commercial product (Tracleer®), the BOS-loaded SNEDDS showed 2.88, 7.63, 3.83, and 4.23 increases in the percentages of cumulative dissolution in fasted state simulated intestinal fluid (FaSSIF), fed state simulated intestinal fluid (FeSSIF), FaSSIF-V2, and FeSSIF-V2, respectively. The ex vivo permeation study showed 12.2-, 19.1-, 20.3-, and 13.1-fold increases in drug permeation in FaSSIF, FeSSIF, FaSSIF-V2, and FeSSIF-V2 for the SNEDDS formulation, as compared to the commercial product, respectively.
Conclusion: Pre-formulation and formulation studies were carried out successfully, and lipid-based optimum BOS-loaded SNEDDS were obtained. The present study confirms the potential of optimum BOS-loaded SNEDDS, which was found to be stable over the long term, to increase the drug's solubility, in vitro dissolution, and ex vivo permeability. This formulation approach has been promising for further in vivo studies, to improve the oral bioavailability of BOS.
Keywords: Bosentan; SNEDDS; experimental design; lipid-based formulation; pre-formulation studies; self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system.
Copyright© 2025 The Author. Published by Galenos Publishing House on behalf of Turkish Pharmacists’ Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yilmaz Usta D, Olgac S, Timur B, Teksin ZS. Development and pharmacokinetic evaluation of Neusilin® US2-based S-SNEDDS tablets for bosentan: fasted and fed states bioavailability, IVIS® real-time biodistribution, and ex-vivo imaging. Int J Pharm. 2023;643:123219. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Timur B, Yilmaz Usta D, Teksin ZS. Investigation of the effect of colloidal structures formed during lipolysis of lipid-based formulation on exemestane permeability using thein vitro lipolysis-permeation model. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2022;77:103797.
-
- Sajedi-Amin S, Barzegar-Jalali M, Fathi-Azarbayjani A, Kebriaeezadeh A, Martínez F, Jouyban A. Solubilization of bosentan using ethanol as a pharmaceutical cosolvent. J Mol Liq. 2017;232:152–158.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
