Immune-regulating extracellular vesicles: a new frontier in autoimmune disease therapy
- PMID: 40366303
- PMCID: PMC12224888
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20253016
Immune-regulating extracellular vesicles: a new frontier in autoimmune disease therapy
Abstract
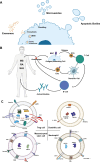
Immune regulation is recognized as a cornerstone therapeutic strategy for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases. These disorders, driven by dysregulated immune responses, contribute significantly to morbidity and mortality. Although conventional immunosuppressive therapies provide symptomatic relief, their prolonged use is often associated with severe adverse effects, underscoring the need for safer and more effective treatment approaches. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), derived from immunoregulatory cells such as regulatory T cells, dendritic cells, mesenchymal stem cells, and neutrophils, have emerged as promising candidates for targeted immunomodulation. These nanoscale vesicles inherit the immunosuppressive properties of their parental cells, thereby facilitating immune homeostasis while mitigating the risks associated with other cell-based therapies. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in the application of immunoregulatory cell-derived EVs for autoimmune disease treatment, with a particular focus on their mechanisms of action within the immune microenvironment. Finally, we discuss the challenges and potential future directions in the development of EV-based therapies for autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; cell-based therapy; extracellular vesicles; immune regulation.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

