The Effect of Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery on Contractile Function and Symptoms in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction
- PMID: 40367000
- PMCID: PMC12107766
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20240486
The Effect of Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery on Contractile Function and Symptoms in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: The degree of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction is an independent risk factor for poor outcomes in patients with chronic coronary syndrome. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is the standard care for the management of ischemic heart failure to improve symptoms and prognosis. However, the predictors of improvement are still uncertain.
Objective: To assess the effect of myocardial revascularization on LV function and symptoms in patients with CCS and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), as well as to identify the improvement predictors.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data and clinical status of 136 consecutive patients with LVEF<50% that underwent CABG. During clinical follow-up echocardiographic LV function was reassessed at the short-term (3.6 months) and long-term (30.8 months), and compared to baseline.
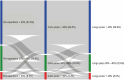
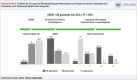
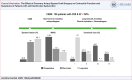
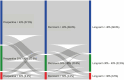
Results: Mean pre-operative LVEF was 40.9 ± 8.6% and wall motion score index (WMSI) was 1.99 ± 0.36, both improving at long-term to 48.1 ± 15.0% (p<0.001) and 1.75 ± 0.49 (p<0.001), respectively. We observed that 55.7% of the patients presented an improvement of LVEF≥10% and 58.1% in WMSI ≥10%. Univariate logistic regression analysis revealed that cerebrovascular disease was the only variable to be predictor of LVEF improvement. At the end of follow-up, we observed a reduction in the rate of patients in functional class III/IV when compared to baseline (65.4 vs. 10.3% - p<0.001).
Conclusions: Patients with CCS and reduced LVEF undergoing CABG experienced improvement in both LV contractile function and size, with beneficial response in functional class.
Fundamento: O grau de disfunção do ventrículo esquerdo (VE) é um fator de risco independente para piores desfechos em pacientes com síndrome coronariana crônica (SCC). A cirurgia de revascularização miocárdica (CRVM) é a estratégia terapêutica padrão na insuficiência cardíaca isquêmica para melhorar os sintomas e o prognóstico. No entanto, os preditores de melhora ainda são incertos.
Objetivos: Avaliar o efeito da revascularização miocárdica sobre a função do VE e sintomas em pacientes com SCC e fração de ejeção do ventrículo esquerdo (FEVE) reduzida, e identificar os preditores de melhora.
Métodos: Analisamos, retrospectivamente, dados e condição clínica de 136 pacientes consecutivos com FEVE <50%, submetidos à CRVM. Durante o acompanhamento ecocardiográfico, a função do VE foi reavaliada no curto (3,6 meses) e longo prazo (30,8 meses), e comparada com os dados basais.
Resultados: A FEVE média no pré-operatório foi 40,9 ± 8,6% e a média do escore do índice de motilidade (WMSI) foi 1,99 ± 0,36, ambos melhorando no longo prazo para 48,1 ± 15,0% (p<0,001) e 1,75 ± 0,49 (p<0,001), respectivamente. Observamos que 55,7% dos pacientes apresentaram uma melhora na FEVE ≥10% e 58,1% no WMSI ≥10%. A análise de regressão logística revelou que a doença cerebrovascular foi a única variável preditora de melhora na FEVE. No final do acompanhamento, observamos uma redução na taxa de pacientes em classe funcional III/IV em comparação ao basal (65,4 vs. 10,3% - p<0,001).
Conclusões: Pacientes com SCC e FEVE reduzida, submetidos à CRVM apresentaram melhora na função contrátil e no tamanho do VE, com resposta benéfica sobre a classe funcional.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does the extended use of arterial grafts compromise the myocardial recovery after coronary artery bypass grafting in left ventricular dysfunction?Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1998 Oct;14(4):353-9. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(98)00219-x. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1998. PMID: 9845138
-
[Surgical revascularization of the myocardium in patients with chronic coronary disease and depressed left ventricular function: 1-year observation].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1998 Jul;100(1):42-9. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1998. PMID: 10085713 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
Prediction of global left ventricular function after bypass surgery in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction. Impact of pre-operative myocardial function, perfusion, and metabolism.Eur Heart J. 2000 Jan;21(2):125-36. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1999.1663. Eur Heart J. 2000. PMID: 10637086
-
Left ventricular recovery after total arterial coronary artery bypass grafting versus conventional coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.Postgrad Med J. 2024 Aug 16;100(1187):671-678. doi: 10.1093/postmj/qgae005. Postgrad Med J. 2024. PMID: 38308654
-
Influence of the preoperative signal-averaged electrocardiogram on left ventricular function after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. The CABG Patch Trial.Am J Cardiol. 1998 Aug 1;82(3):285-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00335-x. Am J Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9708654 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wong M, Staszewsky L, Latini R, Barlera S, Glazer R, Aknay N, et al. Severity of Left Ventricular Remodeling Defines Outcomes and Response to Therapy in Heart Failure: Valsartan Heart Failure Trial (Val-HeFT) Echocardiographic Data. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(11):2022–2027. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.12.053. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

