A pilot pragmatic randomized controlled trial of a 12-month Healthy Lifestyles Program: A collaborative care model for chronic conditions addressing behavioural change
- PMID: 40367102
- PMCID: PMC12077671
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322118
A pilot pragmatic randomized controlled trial of a 12-month Healthy Lifestyles Program: A collaborative care model for chronic conditions addressing behavioural change
Abstract
Background: Lifestyle or behavioural changes can help to address the burden associated with chronic diseases. However, they take time and use of multiple techniques or strategies tailored to a person's needs. The primary objective of this study was to assess the feasibility of the Healthy Lifestyles Program (HLP), a novel 12-month complex intervention based in cognitive behavioural therapy and theories of behaviour change, delivered in a community-based setting in Hamilton, Canada. The secondary objective of the study was to explore implementation factors of the HLP.
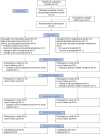
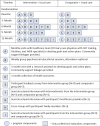
Methods: This pilot pragmatic randomised controlled trial used quantitative and qualitative evaluation methods. Participants were randomly allocated to either intervention group (n = 15) or comparator group (n = 15). The intervention group attended weekly group education sessions and met with the program intervention team monthly to create and review personalized health goals and action plans. The comparator group met with a trained research assistant every three months to develop health goals and action plans. We assessed program feasibility by measuring recruitment, participation and retention rates, missing data, and attendance. Implementation was assessed in accordance with the Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, Maintenance (RE-AIM) framework. Participant-directed and clinical outcome measures were analyzed for between and within group changes using Generalized Estimating Equations (GEE). Thematic analysis was conducted for qualitative data.
Results: Retention rate was 60% (9/15) for the intervention group and 47% (7/15) for the comparator group. Less than 1% of participant-directed and clinical outcomes were missing for those that completed the study. Participants attended an average of 29 of 43 educational sessions and 100% of one-to-one sessions. The program intervention team valued the holistic approach to care, increased time and interaction with participants, professional collaboration, and the ability to provide counselling and health support. Location accessibility was an important factor facilitating implementation. Reducing the number of psycho-social education sessions and having access to a gym could improve retention and program delivery for a larger trial.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the feasibility of the HLP with minor modifications recommended for a larger trial and for the intervention.
Copyright: © 2025 Singh et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Government of Canada. How Healthy are Canadians? A trend analysis of the health of Canadians from a healthy living and chronic disease perspective, P.H.A.o. Canada, Editor. 2017, Government of Canada: Ottawa.
-
- Ronksley P.E., Sanmartin C., Campbell D.J., Weaver R.G., Allan G.M., McBrien K.A., et al. , Perceived barriers to primary care among western Canadians with chronic conditions. Health reports. 2014(4): 3–11. - PubMed
-
- Public Health Ontario. The burden of chronic diseases in Ontario: key estimates to support efforts in prevention. Queen’s Printer for Ontario: Toronto. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous