A roadmap for safe, regulation-compliant Living Labs for AI and digital health development
- PMID: 40367163
- PMCID: PMC12077496
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv7719
A roadmap for safe, regulation-compliant Living Labs for AI and digital health development
Abstract
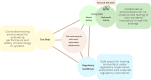
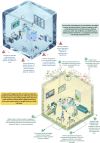
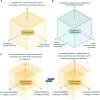
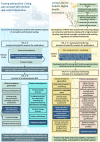
Safe and agile experimentation spaces are essential for developing AI-enabled medical devices and digital health innovations. "Living Labs" offer a collaborative environment for testing technologies in near-real-world settings, capturing user perspectives and outcomes, often missed in traditional testing. However, the flexibility of Living Labs often clashes with the European Union's rigid regulatory frameworks for medical devices that were not designed for digital technologies. We examine this intersection, showing how flexibility in evaluation and patient interaction can coexist with safety guardrails. Our approach integrates technology readiness, preemptive planning, and iterative modifications to bridge innovation and regulation, fostering adaptive health care technology development.
Figures
References
-
- Alowais S. A., Alghamdi S. S., Alsuhebany N., Alqahtani T., Alshaya A. I., Almohareb S. N., Aldairem A., Alrashed M., Bin Saleh K., Badreldin H. A., Al Yami M. S., Al Harbi S., Albekairy A. M., Revolutionizing healthcare: The role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 23, 689 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
-
- N. Gillespie, S. Lockey, C. Curtis, J. Pool, A. Akbari, “Trust in Artificial Intelligence: A global study” (The University of Queensland, KPMG Australia, 2023); https://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ:00d3c94.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

