Identification and characterization of the de novo methyltransferases for eukaryotic N6-methyladenine (6mA)
- PMID: 40367178
- PMCID: PMC12077518
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq4623
Identification and characterization of the de novo methyltransferases for eukaryotic N6-methyladenine (6mA)
Abstract
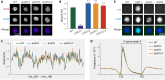
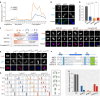
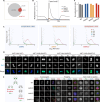
N6-methyladenine (6mA) is an intensively investigated epigenetic modification in eukaryotes. 6mA is maintained through semiconservative transmission during DNA replication, but the identity of de novo methyltransferase (MTase) catalyzing its establishment remains unknown. Here, we identified MT-A70 family proteins AMT2 and AMT5 as the de novo MTases responsible for 6mA establishment, using the unique sexual reproduction process of the unicellular eukaryote Tetrahymena thermophila. Deletion of AMT2 and AMT5 led to a substantial decrease in 6mA levels in the progeny macronucleus, resulting in an altered gene expression pattern and a substantial decline in the survival rate of sexual progenies. Additionally, the maintenance MTase AMT1 could exhibit a much diminished de novo methylation activity in cells lacking AMT2 and AMT5. Our study delineated the establishment-maintenance pathway of 6mA and underscored the biological importance of de novo methylation, revealing a notable parallel between 6mA and the classical 5-methylcytosine in eukaryotes.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang G., Huang H., Liu D., Cheng Y., Liu X., Zhang W., Yin R., Zhang D., Zhang P., Liu J., Li C., Liu B., Luo Y., Zhu Y., Zhang N., He S., He C., Wang H., Chen D., N6-methyladenine DNA modification in Drosophila. Cell 161, 893–906 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

