Phosphorylation by Aurora kinase A facilitates cortical-cytoplasmic dynamics of Par-3 in asymmetric division of radial glia progenitors
- PMID: 40367180
- PMCID: PMC12077515
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq3858
Phosphorylation by Aurora kinase A facilitates cortical-cytoplasmic dynamics of Par-3 in asymmetric division of radial glia progenitors
Abstract
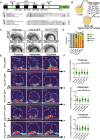
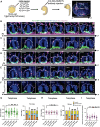
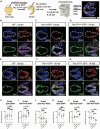
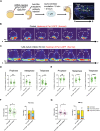
During asymmetric cell division (ACD) of radial glia progenitors (RGPs), the cortical polarity regulator Par-3 is detected in the cytoplasm colocalizing with dynein and Notch ligand DeltaD (Dld). What drives Par-3 to the cytoplasm and its impact on RGP ACD remain unknown. Here, we visualize cytoplasmic Par-3 using in vivo time-lapse imaging and find that Ser954 of zebrafish Par-3 is phosphorylated by Aurora kinase A (AurkA) in vitro. Expression of the nonphosphorylated mutant Par-3S954A dominant negatively affects embryonic development, reduces cytoplasmic Par-3, and disrupts the anteroposterior asymmetry of cortical Par-3 and Dld endosomes and, in turn, daughter cell fate. AurkA in mitotic RGPs shows dynamic pericentrosomal distribution that transiently colocalizes with cortical Par-3 preferentially on the posterior side. AurkA is both necessary and sufficient to increase cytoplasmic while decreasing cortical Par-3, disrupts Par-3 cortical asymmetry, and perturbs polarized Dld endosome dynamics. These findings suggest that AurkA regulates Par-3 cortical-cytoplasmic dynamics that is critical for ACD and daughter cell fate.
Figures



References
-
- Yong K. J., Yan B., The relevance of symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions to human central nervous system diseases. J. Clin. Neurosci. 18, 458–463 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

