A systematic review and meta-analysis of yoga for arterial hypertension
- PMID: 40367243
- PMCID: PMC12077774
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323268
A systematic review and meta-analysis of yoga for arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: This systematic review and meta-analysis is an update to prior research to evaluate the effects of yoga for managing prehypertension and hypertension.
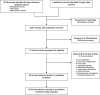
Methods: Medline/PubMed, Scopus and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) were searched from their inception until April 5th 2024. Randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) that compared yoga to any control intervention in participants with diagnosed prehypertension (120-139/80-89 mmHg) or hypertension (≥140/ ≥ 90mmHg) were included. Mean differences (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. Risk of Bias was assessed using the Cochrane tool.
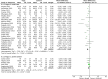
Results: 30 RCTs with 2283 participants were included. Very low quality of evidence was found for positive effects of yoga on systolic blood pressure (SBP, 26 RCTs, n = 2007; MD = -7.95 mmHg, 95% CI = -10.24 to -5.66, p < 0.01), diastolic blood pressure (DBP, 23 RCTs, n = 1836; MD = -4.93 mmHg, 95% CI = -6.25 to -3.60, p < 0.01) and heart rate (HR, 14 RCTs, n = 1118; MD = -4.43 mmHg, 95% CI = -7.36 to -1.50, p < 0.01) compared to waitlist control. Compared to active control, very low quality of evidence was found for positive effects yoga on SBP (5 RCTs, n = 306; MD = -4.16 mmHg, 95%CI = -10.76 to 2.44, p = 0.22), DBP (5 RCTs, n = 306; MD = -1.88 mmHg, 95%CI = -3.41 to -0.36, p = 0.02) and HR (2 RCT, n = 128; MD = -5.16 mmHg, 95% CI = -8.39 to -1.92, p < 0.01). Overall, the studies showed a high degree of heterogeneity. The effects found were robust against selection, detection and attrition bias.
Conclusion: Yoga may be an option for lowering blood pressure in people with prehypertension to hypertension. More and larger high-quality studies are needed to substantiate our findings.
Copyright: © 2025 Geiger et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that no competing interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Statistics 2023 Monitoring health for the SDGs. World Health Organization (WHO); 2023. [cited 2024 May 24]. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gho-documents/world-health...
-
- Mills KT, Bundy JD, Kelly TN, Reed JE, Kearney PM, Reynolds K, et al.. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries. Circulation. 2016;134(6):441-50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018912 PubMed ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4979614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous