Managing an ageing cystic fibrosis population: challenges and priorities
- PMID: 40368426
- PMCID: PMC12076158
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0261-2024
Managing an ageing cystic fibrosis population: challenges and priorities
Abstract
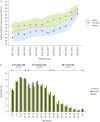
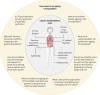
The increasing life expectancy of people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF), largely driven by advancements in early diagnosis, multidisciplinary care and the recent introduction of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulator therapies, is likely to herald a shift in the focus of care toward managing the complexities of ageing. This review highlights key challenges and research priorities for addressing the health needs of an ageing CF population. A growing body of evidence underscores the heightened risks of cancers, cardiovascular diseases and changing nutritional and metabolic profiles as pwCF age. CFTR modulators have improved clinical outcomes, but their effects on inflammation, immunity and long-term disease trajectories remain incompletely understood. Nutritional management, particularly the implications of obesity and body composition, poses new challenges, as does the potential accelerated ageing of immune and pulmonary systems in CF. Emerging issues such as menopause in females with CF, lifetime antimicrobial resistance and the interplay between chronic inflammation and ageing further complicate the care landscape. The review emphasises the urgent need for multidisciplinary research programmes that integrate clinical, patient and community perspectives. Leveraging established CF registries, clinical trial networks and collaborations with ageing research frameworks is critical to addressing these challenges. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that pwCF not only live longer but also experience improved quality of life and holistic wellbeing as they realise the full benefits of therapeutic advances.
Copyright ©The authors 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: F.J. Frost reports research grants from UK Health Security Agency, NIHR Patient Involvement Fund and Cystic Fibrosis Trust; consultancy fees from Insmed; speaker fees from Vertex, AstraZeneca, Gilead and Chiesi; and support for attending meetings from Chiesi and Vertex. D.G. Peckham has no conflicts to declare. I.C. Felton reports speaker fees from Vertex. J.E. Snowball reports speaker fees from Vertex and Chiesi. R.D. Gray reports speaker fees from Vertex. A.M. Jones reports speaker fees from Vertex. N.J. Simmonds reports research grants from Cystic Fibrosis Trust and Vertex Innovation Awards; participation on advisory boards for Vertex, Gilead, Chiesi and Menarini; speaker fees from Vertex, Gilead and Chiesi; and support for attending meetings from Chiesi, Vertex and Pari. R.W. Lord has no conflicts to declare. G.Y.H. Lip reports consultancy and speaker fees from BMS/Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo and Anthos. H. Chandler and K. Murphy have no conflicts to declare. D.G. Downey reports research grants from Chiesi, CF Foundation and CF Trust; consultancy fees from Vertex and Insmed; speaker fees from Chiesi and Gilead; and support for attending meetings from ECFS and CFF. D.N. Sheppard reports research grants from CF Trust and NC3Rs. J.C. Davies reports grants from UK Cystic Fibrosis Trust, CFF, Cystic Fibrosis Ireland, the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council and the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and honoraria from Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eloxx, Algipharma, Abbvie, Arcturus, Enterprise Therapeutics, Recode, LifeArc, Genentech, and Tavanta. J. Bull P. Sommer, B. Cupid and L. Allen have no conflicts to declare. J. Duckers reports grants from UK Cystic Fibrosis Trust, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, Cystic Fibrosis Ireland, EPSRC, NIHR and LifeArc; participation on advisory boards for Chiesi, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eloxx, Algipharma, Abbvie, Arcturus, Enterprise Therapeutics, Recode, LifeArc, Genentech, Tavanta and Insmed; speaker fees from Chiesi, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eloxx, Algipharma, Abbvie, Arcturus, Enterprise Therapeutics, Recode, LifeArc, Genentech, Tavanta and Insmed; and a leadership role as Deputy Editor for the Journal of Cystic Fibrosis and President Elect of the European Cystic Fibrosis Society.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
