Effectiveness of tirzepatide in patients with HFpEF using a target trial emulation retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40368924
- PMCID: PMC12078458
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59616-2
Effectiveness of tirzepatide in patients with HFpEF using a target trial emulation retrospective cohort study
Abstract
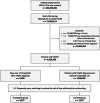
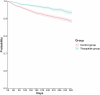
Tirzepatide, a dual agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, has shown promise in improving metabolic and cardiovascular profiles in patients with obesity. However, its potential benefits in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remain unclear. We conducted a real-world, retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX global database. A total of 14,154 patients with HFpEF were included after 1:1 propensity score matching. Tirzepatide use was associated with significantly lower risks of the primary composite outcome of heart failure exacerbation and all-cause mortality (HR 0.52), as well as reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events (HR 0.64) and major adverse kidney events (HR 0.44). Subgroup analyses demonstrated consistent benefits across different strata. Sensitivity analyses using alternative exposure definitions confirmed the robustness of the findings. These results support the potential clinical utility of tirzepatide in HFpEF management and warrant further investigation in randomized controlled trials.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bozkurt, B. et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure: Endorsed by the Canadian Heart Failure Society, Heart Failure Association of India, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and Chinese Heart Failure Association. Eur. J. Heart Fail23, 352–380 (2021). - DOI - PubMed
-
- McDonagh, T. A. et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail.24, 4–131 (2022). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Packer, M., Lam, C. S. P., Lund, L. H., Maurer, M. S. & Borlaug, B. A. Characterization of the inflammatory-metabolic phenotype of heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction: a hypothesis to explain influence of sex on the evolution and potential treatment of the disease. Eur. J. Heart Fail22, 1551–1567 (2020). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

