Subcellular level spatial transcriptomics with PHOTON
- PMID: 40368943
- PMCID: PMC12078482
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59801-3
Subcellular level spatial transcriptomics with PHOTON
Abstract
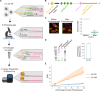
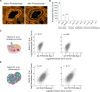
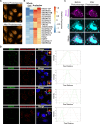
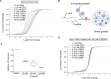
The subcellular localization of RNA is closely linked to its function. Many RNA species are partitioned into organelles and other subcellular compartments for storage, processing, translation, or degradation. Thus, capturing the subcellular spatial distribution of RNA would directly contribute to the understanding of RNA functions and regulation. Here, we present PHOTON, a method which combines high resolution imaging with high throughput sequencing to achieve spatial transcriptome profiling at subcellular resolution. We demonstrate PHOTON as a versatile tool to accurately capture the transcriptome of target cell types in situ at the tissue level such as granulosa cells in the ovary, as well as RNA content within subcellular compartments such as the nucleoli, the mitochondria, and the stress granules. Using PHOTON, we also reveal the functional role of m6A modifications on mRNA partitioning into stress granules. These results collectively demonstrate that PHOTON is a flexible and generalizable platform for understanding subcellular molecular dynamics through the transcriptomic lens.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H.C., S.M.M., and F.C. are on a patent related to this work. F.C. is an academic founder of Curio Biosciences and Doppler Biosciences, and scientific advisor for Amber Bio. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Subcellular Level Spatial Transcriptomics with PHOTON.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 14:2024.09.10.612328. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.10.612328. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 14;16(1):4457. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59801-3. PMID: 39314454 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Fasken, M. B. & Corbett, A. H. Mechanisms of nuclear mRNA quality control. RNA Biol.6, 237–241 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Pamula, M. C. & Lehmann R. How germ granules promote germ cell fate. Nat. Rev. Genet.11, 803–821 2024. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, P. & Kedersha, N. RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.10, 430–436 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

