Prediction model of mitochondrial energy metabolism related genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and its correlation with immune microenvironment
- PMID: 40369105
- PMCID: PMC12078704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-01759-9
Prediction model of mitochondrial energy metabolism related genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and its correlation with immune microenvironment
Abstract
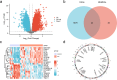
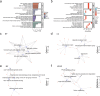
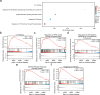
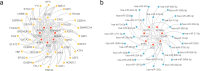
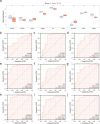
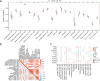
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive lung disease. Recent evidence suggests that the pathogenesis of IPF may involve abnormalities in mitochondrial energy metabolism. This study aimed to identify mitochondrial energy metabolism related differentially expressed genes (MEMRDEGs) and to elucidate their potential mechanistic involvement in IPF. We employed a multistep bioinformatics approach, including data extraction from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, removal of batch effects, and normalization and differential gene expression analyses. We then conducted Gene Ontology, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment, and gene set enrichment analyses. A protein-protein interaction network was constructed from the STRING database, and hub genes were identified. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to evaluate immune infiltration. Our integrated analysis of IPF datasets identified 25 MEMRDEGs. Nine hub genes emerged as central to mitochondrial energy metabolism in IPF. COX5A, EHHADH, and SDHB are potential biomarkers for diagnosing IPF with high accuracy. Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis revealed significant differences in the abundances of specertainfic immune cell types between IPF samples and controls. In conclusion, COX5A, EHHADH, and SDHB are potential biomarkers for the high-accuracy diagnosis of IPF. These findings pave the way for further investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying IPF.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Genes; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Immune microenvironment; Mitochondrial energy metabolism.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contribution of cuproptosis and immune-related genes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 7;16:1458341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1458341. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39991151 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Potential Biomarkers and Pathways for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 4;2021:5545312. doi: 10.1155/2021/5545312. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9848271. doi: 10.1155/2024/9848271. PMID: 34285914 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Integrating machine learning and neural networks for new diagnostic approaches to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and immune infiltration research.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0320242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320242. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273141 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of oxidative stress-related diagnostic markers and immune infiltration features for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by bibliometrics and bioinformatics.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;11:1356825. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1356825. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving genomic approaches to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: moving beyond genes.Clin Transl Sci. 2011 Oct;4(5):372-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2011.00287.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2011. PMID: 22029812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Richeldi, L., Collard, H. R. & Jones, M. G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet389, 1941–1952 (2017). - PubMed
-
- King, T. E. Jr et al. A phase 3 trial of Pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl. J. Med.370, 2083–2092 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Le Pavec, J. et al. Lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Presse Med.49, 104026. 10.1016/j.lpm.2020.104026 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

