Relationships between coping style, life events, and resilience among nurses in China: a cross-sectional study using structural equation modeling
- PMID: 40369562
- PMCID: PMC12076851
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-025-03194-7
Relationships between coping style, life events, and resilience among nurses in China: a cross-sectional study using structural equation modeling
Abstract
Background: Resilience is the ability to adapt and implement effective actions to maintain mental health during adversity, benefiting patients when exhibited by nurses. It encompasses personal and environmental factors. However, few studies have explored their combined impact on nurses' resilience.
Aims: This study investigated the mediating role of coping style in the relationships between life events and resilience among Chinese nurses.
Methods: This study employed a cross-sectional correlational design and followed the STROBE guidelines. Convenience sampling was used to recruit 1,068 clinical nurses from government hospitals in China. Data were collected online using three validated self-reported questionnaires between March and April 2022. Pearson's correlation analysis and structural equation modeling were utilized for data analysis.
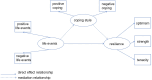
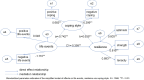
Results: Significant relationships were found between education level, hospital level, professional title, and resilience, as well as between life events, coping style, and resilience. Life events directly and negatively influenced resilience and coping style. Coping style mediated the relationship between life events and resilience.
Conclusions: Nursing managers should provide training to enhance nurses' understanding of mental coping strategies for managing challenges. This will help mitigate the emotional impact of stress, thereby improving nurses' ability to adapt to and implement strategies that promote mental well-being in challenging circumstances.
Keywords: China; Coping style; Life event; Nurse resilience.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: All participants provided written informed consent to participate in this study. The study protocol was approved by the Medical Academy Ethics Board of the Ninth People’s Hospital, Jiaotong University School of Medicine (approval number SHJY20220331). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. State of the world’s nursing report-2020. 2020.
-
- McCann CM, Beddoe E, McCormick K, et al. Resilience in the health professions: a review of recent literature. Int J Wellbeing. 2013;3(1):60–81. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous