The origins and spread of the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) revealed by genomics and seed morphometrics
- PMID: 40370019
- PMCID: PMC12079135
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0198
The origins and spread of the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) revealed by genomics and seed morphometrics
Abstract
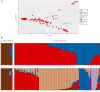
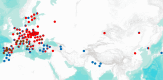
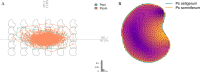
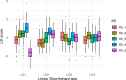
The opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) is one of the most important plants in human history. It is the main source of opiates used as analgesic medicines or psychotropic drugs, the latter related to addiction problems, illegal trafficking and geopolitical issues. Poppyseed is also used in cooking. The prehistoric origins, domestication and cultivation spread of the opium poppy remain unresolved. Traditionally, Papaver setigerum has been considered the wild ancestor with early cultivation presumed to have occurred in the Western Mediterranean region, where setigerum is autochthonous. Other theories suggest that somniferum may have been introduced by Southwest Asian early farmers as a weed. To investigate these hypotheses, we analysed 190 accessions from 15 Papaver species using genotype-by-sequencing and geometric morphometric (GMM) techniques. Our analysis revealed that setigerum is the only taxa genetically close to somniferum and can be better described as a subspecies. The domesticated plants are, however, distinct from setigerum. Additionally, GMM analysis of seeds also revealed morphological differences between setigerum and somniferum. Some phenotypically wild setigerum accessions exhibited intermediate genetic features, suggesting introgression events. Two major populations were found in somniferum and, to some extent, these correspond to differences in seed form. These two populations may reflect recent attempts to breed varieties rich in opiates, as opposed to varieties used for poppyseed production. This study supports the idea that opium poppy cultivation began in the Western Mediterranean, with setigerum as the wild progenitor, although some wild varieties are likely to be feral forms, which can confound domestication studies.This article is part of the theme issue 'Unravelling domestication: multi-disciplinary perspectives on human and non-human relationships in the past, present and future'.
Keywords: agrobiodiversity; domestication; opiates; plant genome; seed morphology.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Morphometrics of waterlogged archaeological seeds give new insights into the domestication and spread of Papaver somniferum L. in Western Europe.PLoS One. 2023 May 25;18(5):e0286190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286190. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37228077 Free PMC article.
-
A morphometric approach to track opium poppy domestication.Sci Rep. 2021 May 7;11(1):9778. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88964-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33963241 Free PMC article.
-
A new minisatellite VNTR marker, Pscp1, discovered for the identification of opium poppy.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2021 Nov;55:102581. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102581. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2021. PMID: 34517229
-
Development of SSR and SNP markers for identifying opium poppy.Int J Legal Med. 2022 Sep;136(5):1261-1271. doi: 10.1007/s00414-022-02810-4. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Int J Legal Med. 2022. PMID: 35316386 Review.
-
Interindividual variability in diabetic patients' response to opium poppy: an overview of impressive factors.Per Med. 2022 Mar;19(2):155-163. doi: 10.2217/pme-2021-0107. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Per Med. 2022. PMID: 35220727 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling domestication: introduction to the theme issue.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 May;380(1926):20240187. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0187. Epub 2025 May 15. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40370018 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Inglis L. 2018. Milk of paradise: a history of opium. London, UK: Macmillan.
-
- Melo D, Álvarez-Ortí M, Nunes MA, Espírito Santo L, Machado S, Pardo JE, Oliveira MBPP. 2022. Nutritional and chemical characterization of poppy seeds, cold-pressed oil, and cake: poppy cake as a high-fibre and high-protein ingredient for novel food production. Foods 11, 3027. (10.3390/foods11193027) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jesus A, Antolín F. 2022. Evidence of the presence and use of neolithic oil plants in the NW of the mediterranean and the Swiss plateau. In The missing woodland resources, pp. 23–40. Kooiweg, The Netherlands: Barkhuis Publishing. (10.2307/j.ctv23wf366.5) - DOI
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations . 2024. Crops and livestock products. See https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed 3 December 2024).
-
- Statista . 2024. Worldwide area for the illegal cultivation of opium poppy from 1994 to 2022. See https://www.statista.com/statistics/268765/area-for-the-illegal-cultivat... (accessed 3 December 2024).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

