Innovative strategies targeting oral microbial dysbiosis: unraveling mechanisms and advancing therapies for periodontitis
- PMID: 40370404
- PMCID: PMC12075390
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1556688
Innovative strategies targeting oral microbial dysbiosis: unraveling mechanisms and advancing therapies for periodontitis
Abstract
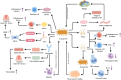
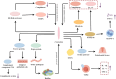
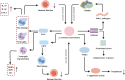
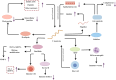
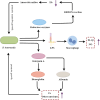
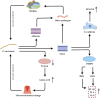
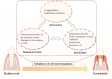
Periodontitis, a prevalent inflammatory oral disease, is intricately linked to disruptions in the oral microbiome, a state known as microbial dysbiosis. This review explores the pivotal roles of key pathogens, including Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia, in driving periodontitis and examines the underlying molecular mechanisms that disrupt microbial homeostasis. We discuss how interactions among bacterial species affect the oral ecosystem's balance and how microbial metabolites influence the host immune responses, contributing to disease progression. Leveraging these insights, we propose cutting-edge therapeutic approaches aimed at restoring microbial equilibrium. These include personalized pharmacological interventions tailored to individual microbiome profiles and innovative microbiome-targeted strategies such as probiotic formulations and bacteriophage therapy. By precisely modulating microbial communities, these strategies hold promise for enhancing treatment efficacy, preventing disease recurrence, and mitigating issues like antimicrobial resistance. Overall, this review paves the way for novel prevention and management techniques in periodontitis, offering significant improvements in oral health outcomes for patients.
Keywords: mechanistic insights; microbial dysbiosis; oral microbiome; periodontitis; therapeutic strategies inflammatory response.
Copyright © 2025 Li, He, Luo, Zhao, Bai and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbial dysbiosis in periodontitis and peri-implantitis: pathogenesis, immune responses, and therapeutic.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 11;15:1517154. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1517154. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40007610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the oral microbiota in the causal effect of adjunctive antibiotics on clinical outcomes in stage III-IV periodontitis patients.Microbiome. 2024 Oct 26;12(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01945-3. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39462428 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of probiotics for preventing dysbiosis in periodontal disease: a randomized controlled trial.Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Dec 7;54(1):357-365. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5798. eCollection 2024. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38812644 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microbiome-based therapies for periodontitis and peri-implantitis.Oral Dis. 2024 Jul;30(5):2838-2857. doi: 10.1111/odi.14782. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Oral Dis. 2024. PMID: 37890080 Review.
-
Porphyromonas Gingivalis in the Development of Periodontitis: Impact on Dysbiosis and Inflammation.Arch Razi Inst. 2022 Oct 31;77(5):1539-1551. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2021.356596.1875. eCollection 2022 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2022. PMID: 37123122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

