A complex role of chromogranin A and its peptides in inflammation, autoimmunity, and infections
- PMID: 40370467
- PMCID: PMC12074958
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567874
A complex role of chromogranin A and its peptides in inflammation, autoimmunity, and infections
Abstract
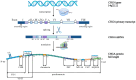
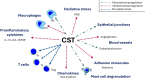
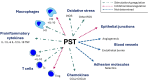
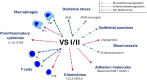
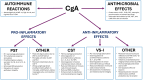
Chromogranin A (CgA), mostly known as a nonspecific neuroendocrine tumor marker, was the first glycoprotein from the granin family characterized as a prohormone for various bioactive peptides including vasostatin I/II (VS-I, VS-II), catestatin (CST), chromofungin (CHR), pancreastatin (PST), WE-14, and others. CgA and its derivatives present various functions, often antagonistic, in maintaining body homeostasis and influencing the immune system. This review aims to summarize the not fully understood role of CgA and its derivatives in inflammation, autoimmunity, and infections. CgA seems to be involved in the complex pathophysiology of cardiovascular disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and other conditions where immune system dysfunction plays a role in the onset and development of the disease (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or rheumatoid arthritis (RA)). However, the direct immunomodulatory role of CgA is difficult to assess since many of its activities may be linked with its peptides. CST and VS-I are considered anti-inflammatory molecules, due to M2 macrophage polarization stimulation and downregulation of certain proinflammatory cytokines. Conversely, PST is reported to stimulate proinflammatory M1 macrophage polarization and Th1 lymphocyte response. Thus, the final effects of CgA in inflammation may depend on its cleavage pattern. Additionally, peptides like CST, VS-I, or CHR exert direct antimicrobial/antifungal activities. CgA, WE-14, and other less-known CgA-derived peptides have also been reported to trigger autoimmune responses, highly studied in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Overall, CgA and its derivatives have an interesting but complex role in immunity, however, their specific roles require further research.
Keywords: WE-14; autoimmune; catestatin (CST); chromofungin (CHR); chromogranin A (CgA); inflammation; pancreastatin (PST); vasostatin (VS).
Copyright © 2025 Maj, Hernik, Tyszkiewicz, Owe-Larsson, Sztokfisz-Ignasiak, Malejczyk and Janiuk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammation Promotes Proteolytic Processing of the Prohormone Chromogranin A by Macrophages.J Endocr Soc. 2025 May 15;9(7):bvaf090. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf090. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Endocr Soc. 2025. PMID: 40458085 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Roles of Chromogranins and Derived Polypeptides in Atherosclerosis, Diabetes, and Coronary Heart Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 6;22(11):6118. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116118. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranin A regulates gut permeability via the antagonistic actions of its proteolytic peptides.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021 Jun;232(2):e13655. doi: 10.1111/apha.13655. Epub 2021 May 6. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 33783968 Free PMC article.
-
Chromogranin A and its fragments in cardiovascular, immunometabolic, and cancer regulation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Nov;1455(1):34-58. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14249. Epub 2019 Oct 6. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 31588572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranin A Regulation of Obesity and Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Feb 8;8:20. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00020. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28228748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blashko G. Structure and function of chromaffin cells. Farmakol Toksikol. (1967) 30:3–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

