Patient-Reported Outcomes During Pelvic Radiation Therapy: A Secondary Analysis on Sexual Function From NRG-RTOG 1203
- PMID: 40370492
- PMCID: PMC12071503
- DOI: 10.1200/OA-24-00088
Patient-Reported Outcomes During Pelvic Radiation Therapy: A Secondary Analysis on Sexual Function From NRG-RTOG 1203
Abstract
Purpose: NRG-RTOG 1203 reported that intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) reduced patient-reported GI toxicities in patients with cervical/endometrial cancer receiving postoperative RT, compared with 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DRT). We conducted a secondary analysis of patient-reported sexual function (PR-SF) among treatment groups to identify factors associated with sexual dysfunction.
Methods and materials: Patients on NRG-RTOG 1203 were randomly assigned to 3DRT versus IMRT and completed Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO)-Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) and FACT-Cx surveys at baseline, week 5 of RT, and at 4-6 weeks, 1 year, and 3 years after RT. Patient responses to FACT-Cx sexual function questions were analyzed. The between-arm frequency and severity of responses and their comparison with PRO-CTCAE GI toxicity were tested using chi-square tests. A repeated-measures logistic regression model was used to determine the impact of clinical and treatment factors on PR-SF.
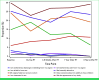
Results: Two hundred thirty-six patients completed PR-SF questions; 125 (53%) received 3DRT and 111 (47%) IMRT. There were no significant differences in PR-SF between groups (P > .05). After RT, responses to "I am afraid to have sex" and "I am interested in sex" significantly improved over time (P = .007 and P = .03, respectively). At 1 year after RT, women with interference from abdominal pain were more bothered by odor from the vagina versus women with no interference of abdominal pain (5% v 0%, P = .006). Additionally, at 1 year after RT, women with no severity of abdominal pain or no interference from abdominal pain liked their body appearance more versus women with at least some abdominal pain or some interference from abdominal pain (34% v 13%, P = .003 and 32% v 6%, P = .001, respectively).
Conclusion: PR-SF was similar between treatment groups. After RT, fear of sex declined and interest in sex improved over time. Women with GI toxicity after RT completion are at risk for worse sexual function.
© 2025 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to https://ascopubs.org/authors. Ann H. Klopp Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: UTSC.P1380US, US Patent Application No. 17/642,654, based on International Patent Application No. PCT/US2020/050285, titled “Methods and Compositions for the Treatment of HPV-Related Cancer” by Ann Klopp et al J. Spencer Thompson Employment: OU HEalth Desiree E. Doncals Research Funding: Summa Health System, PreludeDx Vijayananda Kundapur Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: I hold a US patent for “mini beam collimator for medical linear accelerators” Patent No.: US 10,702,711 B2 Date of Patent: July 7, 2020 I also hold a Canadian patent for “mini beam collimator for medical linear accelerators” Patent number 2,989,042. Date of patent: December 8, 2020 Dasarahally S. Mohan Employment: The Permanente Medical Group Sharad A. Ghamande Consulting or Advisory Role: Genentech Speakers' Bureau: Tesaro/GSK Research Funding: Jounce Therapeutics (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Akeso Biopharma (Inst), Merck Serono (Inst), Incyte (Inst), Ellipses Pharma (Inst), Aravive (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Merck (Inst), Roche (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Takeda (Inst), Seagen (Inst), Advaxis (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Clovis Oncology (Inst), AbbVie (Inst), Tesaro (Inst) Shannon N. Westin Consulting or Advisory Role: Roche, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Medscape, Clovis Oncology, Gerson Lehrman Group, Merck, OncLive, Targeted Oncology, Curio Science, GlaxoSmithKline, Eisai, Zentalis, EQRX, Lilly, Vincerx Pharma, Mereo BioPharma, Immunogen, Mersana, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Caris Life Sciences, Nuvectis Pharma, Seagen, Immunocore, ZielBio, Verastem, Gilead Sciences, Mersana, Nuvectis Pharma, pharma&, Daiichi Sankyo, Loxo/Lilly, Incyte Research Funding: AstraZeneca (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Clovis Oncology (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), GOG Foundation (Inst), Mereo BioPharma (Inst), Bio-Path Holdings, Inc (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Zentalis (Inst), Avenge Bio (Inst), Jazz Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Nuvectis Pharma (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Loxo/Lilly (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo Europe GmbH (Inst) Kara L. Schnarr Consulting or Advisory Role: Merck David K. Gaffney Consulting or Advisory Role: Merck Research Funding: Elekta Steven E. Waggoner Research Funding: Trillium Therapeutics (Inst), Genentech (Inst) Stephanie L. Pugh Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Janssen (Inst) Lisa A. Kachnic Honoraria: Varian Medical Systems Consulting or Advisory Role: New B Innovation Research Funding: Varian Medical Systems (Inst) Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: UpToDate Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Varian Medical Systems Uncompensated Relationships: RTOG Foundation, NRG Oncology, SWOG No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Mundt AJ, Roeske JC, Lujan AE: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy in gynecologic malignancies. Med Dosim 27:131-136, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Greven K, Winter K, Underhill K, et al. : Preliminary analysis of RTOG 9708: Adjuvant postoperative radiotherapy combined with cisplatin/paclitaxel chemotherapy after surgery for patients with high-risk endometrial cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:168-173, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Hasselle MD, Rose BS, Kochanski JD, et al. : Clinical outcomes of intensity-modulated pelvic radiation therapy for carcinoma of the cervix. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80:1436-1445, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Yeung AR, Pugh SL, Klopp AH, et al. : IMRT improves late toxicity compared to conventional RT: An update on NRG Oncology-RTOG 1203. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 105:S50, 2019
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
