Unraveling the role of histone acetylation in sepsis biomarker discovery
- PMID: 40370519
- PMCID: PMC12074977
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1582181
Unraveling the role of histone acetylation in sepsis biomarker discovery
Abstract
Introduction: Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection. Despite advances in clinical care, effective biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis remain lacking. Emerging evidence suggests that histone acetylation plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of sepsis.
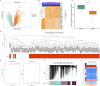
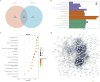
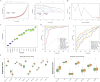
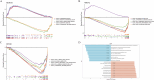
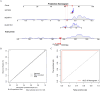
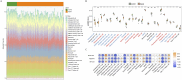
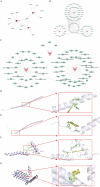
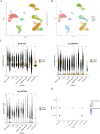
Methods: Transcriptomic and single-cell RNA sequencing data were used to identify histone acetylation-related genes. Differential expression analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were performed, followed by machine learning algorithms (LASSO, SVM-RFE, and Boruta) to screen for potential biomarkers. Mendelian randomization (MR), RT-qPCR, and functional assays were conducted for validation.
Results: BLOC1S1, NDUFA1, and SFT2D1 were identified as key biomarkers. A predictive nomogram demonstrated strong diagnostic potential. Immune infiltration and single-cell analyses linked the biomarkers to macrophage activity. MR analysis confirmed SFT2D1 as a causal factor in sepsis. Functional assays showed that knockdown of SFT2D1 suppressed CXCL10 and IL-6 expression, indicating its pro-inflammatory role.
Discussion: This study identifies novel biomarkers associated with histone acetylation and immune dysregulation in sepsis. These findings deepen our understanding of sepsis pathogenesis and may facilitate the development of improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; biomarkers; histone acetylation; sepsis; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Deng, Du, Li, Qiu, Zhu, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 7;26(9):4433. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094433. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362669 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of m6A RNA methylation and ferroptosis-related biomarkers in sepsis: transcriptome combined with single-cell RNA sequencing.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 7;16:1543517. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543517. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40124361 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of pyroptosis-related genes and natural killer T cells in sepsis pathogenesis: a comprehensive bioinformatics and Mendelian randomization analysis.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;76(2). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2025.2.10. Epub 2025 May 5. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40350654
-
Comprehensive integration of diagnostic biomarker analysis and immune cell infiltration features in sepsis via machine learning and bioinformatics techniques.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 10;16:1526174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526174. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40129981 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic stratification of sepsis through DNA damage response based RiskScore system: insights from single-cell RNA-sequencing and transcriptomic profiling.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 9;15:1345321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1345321. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38404591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen B., Zhou M., Guo L., Huang H., Sun X., Peng Z., et al. (2024b). An integrated machine learning framework identifies prognostic gene pair biomarkers associated with programmed cell death modalities in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 29 (3), 121. 10.31083/j.fbl2903121 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

