Effective therapeutic targeting of tumor lineage plasticity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer by BRD4 inhibitors
- PMID: 40370549
- PMCID: PMC12069891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.01.007
Effective therapeutic targeting of tumor lineage plasticity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer by BRD4 inhibitors
Abstract
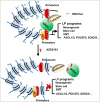
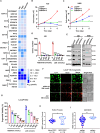
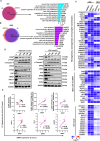
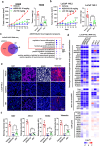
Tumor lineage plasticity (LP) is an emerging hallmark of cancer progression. Through pharmacologically probing the function of epigenetic regulators in prostate cancer cells and organoids, we identified bromodomain protein BRD4 as a crucial player. Integrated ChIP-seq and RNA-seq analysis of tumors revealed, for the first time, that BRD4 directly activates hundreds of genes in the LP programs which include neurogenesis, axonogenesis, EMT and stem cells and key drivers such as POU3F2 (BRN2), ASCL1/2, NeuroD1, SOX2/9, RUNX1/2 and DLL3. Interestingly, BRD4 genome occupancy is reprogrammed by anti-AR drugs from facilitating AR function in CRPC cells to activating the LP programs and is facilitated by pioneer factor FOXA1. Significantly, we demonstrated that BRD4 inhibitor AZD5153, currently at clinical development, possesses potent activities in complete blockade of tumor growth of both de novo neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) and treatment-induced NEPC PDXs and that suppression of tumor expression of LP programs through reduction of local chromatin accessibility is the primary mechanism of action (MOA) by AZD5153. Together, our study revealed that BRD4 plays a fundamental role in direct activation of tumor LP programs and that its inhibitor AZD5153 is highly promising in effective treatment of the lethal forms of the diseases.
Keywords: AZD5153; BRD4; BRN2; ChIP-seq; FOXA1; Neurogenesis; PDX; Tumor lineage plasticity.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BET Bromodomain Inhibition Blocks an AR-Repressed, E2F1-Activated Treatment-Emergent Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Lineage Plasticity Program.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 1;27(17):4923-4936. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4968. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34145028 Free PMC article.
-
AZD5153, a Bivalent BRD4 Inhibitor, Suppresses Hepatocarcinogenesis by Altering BRD4 Chromosomal Landscape and Modulating the Transcriptome of HCC Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 24;10:853652. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.853652. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35399501 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Biological Features of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2021 Jan 12;23(2):15. doi: 10.1007/s11912-020-01003-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33433737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Master Neural Transcription Factor BRN2 Is an Androgen Receptor-Suppressed Driver of Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Prostate Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2017 Jan;7(1):54-71. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-1263. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 27784708
-
The Role of Epigenetic Change in Therapy-Induced Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Lineage Plasticity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 14;13:926585. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.926585. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ogawa S. Targeting lineage plasticity overcomes chemoresistance. Cancer Cell. 2022;40:905–907. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

