Tuning and validation of a virtual mechanical testing pipeline for condylar stress fracture risk assessment in Thoroughbred racehorses
- PMID: 40370600
- PMCID: PMC12077239
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.241935
Tuning and validation of a virtual mechanical testing pipeline for condylar stress fracture risk assessment in Thoroughbred racehorses
Abstract
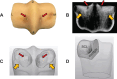
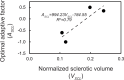
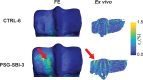
Condylar stress fracture of the third metacarpal/metatarsal bone (MC3/MT3) in Thoroughbred racehorses is a common catastrophic injury, putting both the racehorse and the jockey at risk. Microdamage forms in the distal MC3 and may result in strain elevation and higher risk of stress fracture, directly and through focal osteolysis resulting from the associated damage repair by remodelling in the condylar parasagittal grooves (PSG). Standing computed tomography (sCT) is a practical screening tool for detecting fatigue-induced structural changes, but clinical interpretation remains subjective. The goal of this study was to develop and validate an sCT-based, subject-specific finite element analysis pipeline for virtual mechanical testing of the distal MC3. Twelve (n = 12) MC3 condyles with available ex vivo strain were selected. Half of the specimens were used for tuning Young's modulus in fatigue sites, and the other half were used to evaluate the validity of the pipeline in predicting PSG strain. The tuned model improved the prediction of strain and predicted higher strain in bones with PSG lysis over the untuned model, which is an essential feature for a diagnostic screening tool. The presented pipeline can assist clinicians with the interpretation of sCT-detectable structural changes and, ultimately, with the assessment of condylar fracture risk in racing Thoroughbreds.
Keywords: Thoroughbred racehorses; condylar stress fracture; finite element analysis; functional adaptation; third metacarpal bone.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
P.M. is a co-founder and the Chief Medical Officer of Asto CT Inc., a subsidiary of Centaur Health Holdings Inc. and founder of Eclipse Consulting LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subchondral bone fatigue injury in the parasagittal condylar grooves of the third metacarpal bone in thoroughbred racehorses elevates site-specific strain concentration.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024 Jul;155:106561. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2024.106561. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024. PMID: 38678748
-
Comparison of radiography and computed tomography for identification of third metacarpal structural change and associated assessment of condylar stress fracture risk in Thoroughbred racehorses.Equine Vet J. 2025 May;57(3):723-736. doi: 10.1111/evj.14131. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Equine Vet J. 2025. PMID: 39143731 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomographic imaging of subchondral fatigue cracks in the distal end of the third metacarpal bone in the thoroughbred racehorse can predict crack micromotion in an ex-vivo model.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 31;9(7):e101230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101230. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25077477 Free PMC article.
-
Fractures--a preventable hazard of racing thoroughbreds?Vet J. 2002 Jan;163(1):19-29. doi: 10.1053/tvjl.2001.0610. Vet J. 2002. PMID: 11749133 Review.
-
Aetiopathogenesis of parasagittal fractures of the distal condyles of the third metacarpal and third metatarsal bones--review of the literature.Equine Vet J. 1999 Mar;31(2):116-20. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1999.tb03803.x. Equine Vet J. 1999. PMID: 10213423 Review.
References
-
- Peloso JG, Vogler III JB, Cohen ND, Marquis P, Hilt L. 2015. Association of catastrophic biaxial fracture of the proximal sesamoid bones with bony changes of the metacarpophalangeal joint identified by standing magnetic resonance imaging in cadaveric forelimbs of Thoroughbred racehorses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 246, 661–673. ( 10.2460/javma.246.6.661) - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

