Efficacy and safety of furmonertinib in patients with EGFR‑mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma after failure of multiple lines of therapy: A single‑center retrospective study
- PMID: 40370648
- PMCID: PMC12076557
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2025.15074
Efficacy and safety of furmonertinib in patients with EGFR‑mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma after failure of multiple lines of therapy: A single‑center retrospective study
Abstract
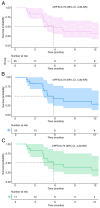
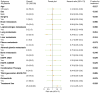
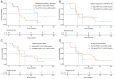
Currently, treatments for patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are limited after receiving multiple lines of therapy. Furmonertinib, a newly developed third-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), has shown potential as a subsequent treatment. To explore efficacy and safety of furmonertinib, the present retrospective study analyzed patients with EGFR-mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) who received furmonertinib after the failure of multiple lines of therapy at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital (Beijing, China) between December 2021 and April 2024. Data on patient demographics, treatment efficacy and safety outcomes were assessed until disease progression. A total of 25 patients with advanced LUAD were retrospectively included in the analysis. Among them, 15 (60.0%) harbored exon 19del, whilst 10 (40.0%) had exon21 L858R mutations. Pre-treatment genetic testing was performed in 14 patients (56.0%). Prior to furmonertinib therapy, 17, 5 and 19 patients had previously received first-, second- and third-generation EGFR-TKIs, respectively. The median line of treatment before furmonertinib was 3. The median progression-free survival was 5.73 (95% confidence interval, 4.30-not reached) months. The objective response rate was 16.0% (n=4) and the disease control rate was 88.0% (n=22). A total of 18 (72.0%) patients experienced at least one adverse event (AE). The rate of AEs was 80.0% (n=20) for grade 1-2, and 20.0% (n=5) for grade 3-4 AEs. No AEs led to treatment discontinuation, dose reductions or death. In conclusion, furmonertinib is a viable treatment option for patients with EGFR-mutant advanced LUAD after the failure of multiple lines of therapy, even after resistance to treatment with third-generation EGFR-TKIs targeted agents. However, further large-scale clinical studies are warranted to validate these findings.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors; furmonertinib; lung adenocarcinoma; multiple lines of therapy; targeted therapies.
Copyright: © 2025 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of re-challenging 160 mg furmonertinib for advanced NSCLC after resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs targeted agents: A real-world study.Lung Cancer. 2023 Oct;184:107346. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107346. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Lung Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37604026
-
Efficacy, safety, and genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2b, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Aug;9(8):829-839. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30455-0. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33780662 Clinical Trial.
-
EGFR exon 20 insertions mutation in lung adenocarcinoma and its response by high-dose of Furmonertinib: a real-world study.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 20;25(1):900. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14313-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40394562 Free PMC article.
-
First report of furmonertinib as a first-line treatment in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations after the kinase domain αC-helix: Two case reports and a literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 29;102(52):e36667. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036667. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38206746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Furmonertinib for EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a glittering diamond in the rough of EGFR-TKI.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1357913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1357913. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38440180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ding PN, Becker TM, Bray VJ, Chua W, Ma YF, Lynch D, Po J, Luk AWS, Caixeiro N, de Souza P, Roberts TL. The predictive and prognostic significance of liquid biopsy in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective study. Lung Cancer. 2019;134:187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.06.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Au JSK, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G, Yang PC. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER) J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:154–162. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
