Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as advanced polymeric scaffolds for efficient cancer chemotherapy: recent progress and challenges
- PMID: 40370857
- PMCID: PMC12076205
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra00948k
Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as advanced polymeric scaffolds for efficient cancer chemotherapy: recent progress and challenges
Abstract
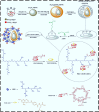
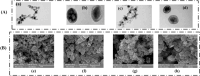
Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MMS NPs) stand out as excellent options for targeted chemotherapy owing to their remarkable features, such as extensive surface area, substantial pore volume, adjustable and uniform pore size, facile scalability, and versatile surface chemistry. This review comprehensively explores the latest developments in MMS NPs, emphasizing their design, functionalization, and application in cancer therapy. Initially, we discuss the critical need for targeted and controlled drug delivery (DD) in oncology, highlighting the role of magnetic and MMs in addressing some challenges. Subsequently, the key features of MMS NPs, such as their high surface area, pore structure, and functionalization strategies, are examined for their impact on their DD performance for efficient cancer chemotherapy. The integration of chemotherapy methods such as photothermal therapy and photodynamic therapy with MMS NPs is also explored, showcasing multifunctional platforms that combine imaging and therapeutic capabilities. Finally, we identify the current challenges and provide future perspectives for the development and clinical translation of MMS NPs, underscoring their potential to reshape CT paradigms.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Adv Mater. 2013 Jun 18;25(23):3144-76. doi: 10.1002/adma.201205292. Epub 2013 May 17. Adv Mater. 2013. PMID: 23681931 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: facile surface functionalization and versatile biomedical applications in oncology.Acta Biomater. 2020 Oct 15;116:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32911102 Review.
-
Gadolinium-incorporated mesoporous silica nanoparticles.2011 Jul 11 [updated 2011 Aug 10]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Jul 11 [updated 2011 Aug 10]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21850780 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Nanosilica: Recent Progress in Synthesis, Functionalization, Biocompatibility, and Biomedical Applications.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019 Oct 14;5(10):4882-4898. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00464. Epub 2019 Sep 27. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019. PMID: 33455238
-
Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for potential delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and hyperthermia.Dalton Trans. 2014 Nov 7;43(41):15482-90. doi: 10.1039/c4dt01984a. Dalton Trans. 2014. PMID: 25190592
Cited by
-
Applications of Tailored Mesoporous Silicate Nanomaterials in Regenerative Medicine and Theranostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 16;26(16):7918. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167918. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fan W. Yung B. Huang P. Chen X. Chem. Rev. 2017;117:13566–13638. - PubMed
-
- Foroozandeh A. Abdouss M. SalarAmoli H. Pourmadadi M. Yazdian F. Process Biochem. 2023;127:82–91.
-
- Foroozandeh A. SalarAmoli H. Abdouss M. Pourmadadi M. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2024;7:100195.
-
- Thakor A. S. Gambhir S. S. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2013;63:395–418. - PubMed
-
- Li M. C. JAMA. 1960;174:1291. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

