Multicomponent catalyst-free regioselective synthesis and binding studies of 3-aroyl-2-methylimidazo[1,2- a]pyrimidines with BSA using biophysical and computational techniques
- PMID: 40370858
- PMCID: PMC12076138
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra01795e
Multicomponent catalyst-free regioselective synthesis and binding studies of 3-aroyl-2-methylimidazo[1,2- a]pyrimidines with BSA using biophysical and computational techniques
Abstract
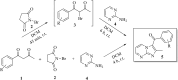
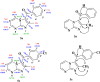
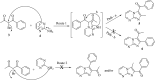
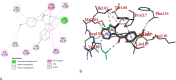
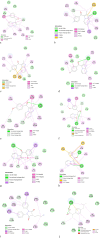
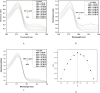
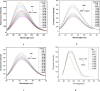
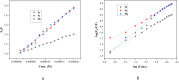
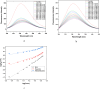
A facile and environmentally benign protocol for regioselective synthesis of diversely substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines 5a-h has been described via multicomponent reaction of unsymmetrical β-diketones 1, N-bromosuccinimide 2 and 2-aminopyrimidine 4 in DCM. The reaction proceeds through in situ formation of α-bromo-β-diketones 3 and their ensuing condensation with 2-aminopyrimidine without the need of any organic or inorganic catalyst. The structure of the regioisomeric product was characterized by 1H, 13C NMR, heteronuclear 2D NMR and HRMS studies. The present protocol offers several advantages such as avoidance of metal-based and toxic catalysts, broad substrate scope with respect to substitutions on β-diketones, operational simplicity, easy work-up and high yields. Computational molecular docking studies were carried out to examine the interaction of imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines with bovine serum albumin (BSA). Moreover, different spectroscopic approaches viz. UV-visible, steady-state fluorescence and competitive displacement assays were carried out to investigate the binding mechanisms of imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines (5c, 5e and 5h) with BSA. The results thus obtained revealed that imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines showed moderate binding with BSA through a static quenching mechanism and compound 5e had more affinity to bind in site I of BSA.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) confirm that this article's content has no conflict of interest.
Figures
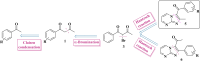
Similar articles
-
Visible-light driven regioselective synthesis, characterization and binding studies of 2-aroyl-3-methyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidines with DNA and BSA using biophysical and computational techniques.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 11;11(1):22135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01037-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34764313 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and characterization of tetra substituted 2,3-dihydrothiazole derivatives as DNA and BSA targeting agents: advantages of the visible-light-induced multicomponent approach.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 22;14(32):23152-23176. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02331e. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39040709 Free PMC article.
-
Visible Light-Prompted Regioselective Synthesis of Novel 5-Aroyl/hetaroyl-2',4-dimethyl-2,4'-bithiazoles as DNA- and BSA-Targeting Agents.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Nov 13;24(11):4798-4818. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00554. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 37729507
-
An expeditious on-water regioselective synthesis of novel arylidene-hydrazinyl-thiazoles as DNA targeting agents.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jul;136:106524. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106524. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37079989
-
Interaction mechanism of a pesticide, Azoxystrobin with bovine serum albumin: Assessments through fluorescence, UV-Vis absorption, electrochemical and molecular docking simulation techniques.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 Mar 5;308:123719. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2023.123719. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024. PMID: 38064964
References
-
- Doganc F. Aydin A. S. Şahin E. Göker H. Regioselective N-alkylation of some 2 or 6-chlorinated purine analogues. J. Mol. Struct. 2023;1272:134200. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134200. - DOI
-
- Ramírez-Trinidad Á. Carrillo-Jaimes K. Rivera-Chávez J. A. Hernández-Vázquez E. Synthesis and cytotoxic/antimicrobial screening of 2-alkenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines. Med. Chem. Res. 2023;32(1):144–157. doi: 10.1007/s00044-022-02997-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

