Predictive Value of IL-6 and PDGF-AA for 28-Day Mortality Risk in Critical Ill Patients
- PMID: 40370968
- PMCID: PMC12075949
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S512295
Predictive Value of IL-6 and PDGF-AA for 28-Day Mortality Risk in Critical Ill Patients
Abstract
Background: Identification of prognostic biomarkers for critical illness are essential to improving mortality in the context of precision medicine. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and platelet-derived growth factor AA(PDGF-AA) in predicting 28-day mortality in critically ill patients.
Methods: 199 critically ill patients were recruited from the emergency department of the Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, between October 2020 and April 2021. IL-6, PDGF-AA and other markers were tested immediately, and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) scores were calculated within 24h of admission to the emergency department. Patients were divided into survival and non-survival groups according to clinical outcomes for 28 days. The quantitative detections of IL-6 and PDGF-AA were performed using the Luminex assay. Spearman correlation, logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analyses were conducted for comparison.
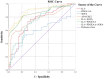
Results: Among 199 patients, 139 died and 60 survived within 28 days, IL-6 and PDGF-AA levels were higher in the non-survival group (P<0.05). IL-6 levels correlated with PDGF-AA levels in the non-survival group (P<0.001). IL-6 and PDGF-AA were independent predictors off 28-day mortality in critically ill patients (OR=1.003, 1.002). Combination of IL-6 and SOFA can make an AUROC of 0.892 with a specificity of 91.4%. Combination of IL-6, PDGF-AA and SOFA can make an AUROC of 0.905 with a specificity of 91.5%.
Conclusion: This study highlights the importance of monitoring serum levels of IL-6 and PDGF-AA in critically ill patients. Compared with the marker alone, combinations with other conventional risk factors have better predictive values.
Keywords: APACHE II; Critical illness; IL-6; PDGF-AA; SOFA.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Value of Heart-Type Fatty Acid-Binding Protein for Mortality Risk in Critically Ill Patients.Dis Markers. 2022 Dec 27;2022:1720414. doi: 10.1155/2022/1720414. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36605375 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern of serum interleukin-7 in elderly septic patients and its prognostic value for predicting short-term mortality.Cytokine. 2024 Aug;180:156664. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156664. Epub 2024 May 24. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 38795605
-
[The prognostic value of serum procalcitonin on severity of illness in non-sepsis critically ill patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 Aug;28(8):688-93. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2016.08.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 27434557 Chinese.
-
Prognostic Value of Admission Lactate Levels in Critically Ill Patients: A Comparative Study With Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II Scores.Cureus. 2024 Oct 13;16(10):e71372. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71372. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39539913 Free PMC article.
-
[Early lactate/albumin ratio combined with quick sequential organ failure assessment for predicting the prognosis of sepsis caused by community-acquired pneumonia in the emergency department].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):118-122. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240709-00577. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017357 Chinese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous