Transcriptome Analysis to Elucidate the Response of Sanghuangporus baumii (Pilát) L.W. Zhou & Y.C. Dai to Sodium Treatment
- PMID: 40371011
- PMCID: PMC12077424
- DOI: 10.1080/12298093.2025.2500194
Transcriptome Analysis to Elucidate the Response of Sanghuangporus baumii (Pilát) L.W. Zhou & Y.C. Dai to Sodium Treatment
Abstract
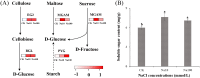
To investigate the effects and underlying mechanisms of sodium (Na+) on the growth characteristics of Sanghuangporus baumii mycelia, a single-factor Na+ addition experiment was performed. We found that treatment with 10 mmol/L Na+ (Na10) significantly increased the growth rate (0.41 ± 0.01 cm/d) and biomass (4.27 ± 0.05 g/L) of S. baumii mycelia, surpassing the control (Ck) group by 3.14% and 4.06%, respectively. In contrast, treatment with 100 mmol/L Na+ (Na100) resulted in a significant reduction in growth rate (0.34 ± 0.01 cm/d) and biomass (3.25 ± 0.02 g/L) of S. baumii mycelia compared to the Ck group. Transcriptome analysis further revealed that low Na+ concentrations (10 mmol/L) promoted the accumulation of soluble sugars (7.63 ± 0.54 mg/g) and upregulated the expression of pertinent genes, thereby accelerating mycelial growth. On the other hand, high Na+ concentrations (100 mmol/L) led to H2O2 accumulation (12.18 ± 0.24 μmol/g), causing toxicity in S. baumii mycelia. High Na+ concentrations also significantly boosted the production of valuable metabolites, such as triterpenoids (19.65 ± 0.22 mg/g), although the exact mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Overall, we suggest an effective approach for accelerating mycelial growth cycles and enhancing the production of high-value bioactive compounds from S. baumii.
Keywords: Sanghuangporus baumii; peroxisome pathway; sodium; starch and sucrose metabolism; triterpenoids.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of the Korean Society of Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Calcium-Induced Regulation of Sanghuangporus baumii Growth and the Biosynthesis of Its Triterpenoids.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;11(3):238. doi: 10.3390/jof11030238. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137275 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Phenolic Acids Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Triple Quadrupole (UHPLC-QqQ) in Fruiting Bodies of Sanghuangporus baumii (Pilát) L.W. Zhou and Y.C. Dai.Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 13;12(20):3565. doi: 10.3390/plants12203565. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37896027 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into Methyl Jasmonate Regulation of Triterpenoid Biosynthesis in Medicinal Fungal Species Sanghuangporusbaumii (Pilát) L.W. Zhou & Y.C. Dai.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Aug 23;8(9):889. doi: 10.3390/jof8090889. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135614 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Response of Sanghuangporus baumii to Zn2+ Induction and Biosynthesis of a Key Pharmacological Component: Triterpenoid.Microorganisms. 2025 May 3;13(5):1067. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051067. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431240 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Analysis of Lanosterol Synthase Gene in Dynamic Accumulation of Triterpenoids in Sanghuangporus baumii.Protein Pept Lett. 2022;29(1):37-45. doi: 10.2174/0929866528666210922103059. Protein Pept Lett. 2022. PMID: 34551686
References
-
- Xue Q, Sun J, Zhao MW, et al. . Immunostimulatory and anti-tumor activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii mycelia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;27(5):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.046. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
