Renal function and efficacy of dual antiplatelet vs. alteplase in minor stroke: a post hoc analysis of ARAMIS study
- PMID: 40371069
- PMCID: PMC12075944
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1568711
Renal function and efficacy of dual antiplatelet vs. alteplase in minor stroke: a post hoc analysis of ARAMIS study
Abstract
Background: This secondary analysis of the ARAMIS trial evaluated renal function's modifying effects on therapeutic responses to dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) versus intravenous thrombolysis in acute minor ischemic stroke.
Methods: Based on the as-treated set, we stratified patients by admission estimated glomerular filtration rate into three groups: normal renal function (≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2), mildly decreased renal function (eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2), and moderate to severe impairment renal function group (<60 mL/min/1.73 m2). The primary endpoint was excellent functional outcome defined as a modified Rankin Scale score of 0-1 at 90 days.
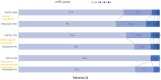
Results: Among 615 analyzed patients, 367 (59.7%) exhibited normal renal function, 209 (34.0%) exhibited mildly decreased renal function and 39 (6.3%) exhibited moderate to severe impairment renal function. A numerically higher rate of excellent functional outcome was found in normal renal function patients with DAPT vs. alteplase (94.4% vs. 90.4%; p = 0.147), while no intergroup difference emerged in mildly decreased renal function patients (93.9% vs. 93.7%; p = 0.958) and moderate to severe impairment renal function patients (93.8% vs. 95.7%; p = 0.792). There was no significant interaction between treatment and renal function on the primary outcome (adjusted interaction p = 0.337).
Conclusion: Among patients with normal renal function, DAPT was associated with a numerically higher, but not statistically significant, rate of excellent functional outcome in patients with minor nondisabling acute ischemic stroke presenting within 4.5 h of symptom onset compared with alteplase.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT03661411.
Keywords: clinical outcome; dual antiplatelet; intravenous thrombolysis; minor stroke; renal function.
Copyright © 2025 He, He and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khatri P, Kleindorfer DO, Devlin T, Sawyer RN, Jr, Starr M, Mejilla J, et al. . Effect of alteplase vs aspirin on functional outcome for patients with acute ischemic stroke and minor nondisabling neurologic deficits: the PRISMS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2018) 320:156–66. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.8496, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous